
 Back in April last year, we wrote an article about teaching children to grow food like vegetables and herbs at home — and its many benefits. It turned out to be enormously popular, so today we follow up with a guide to growing microgreens, for children. This activity is great fun, very educational and the result is extremely nutritious food!
Back in April last year, we wrote an article about teaching children to grow food like vegetables and herbs at home — and its many benefits. It turned out to be enormously popular, so today we follow up with a guide to growing microgreens, for children. This activity is great fun, very educational and the result is extremely nutritious food!
What Are Microgreens?
Also known as micro leaves, microgreens are an easy-to-grow crop that can be grown by children and parents any time of year. What’s more, they can be grown indoors, without needing much room, and all at negligible cost. Take a look at the photos and you’ll soon get the idea of what type of crop they are; they’re basically the very young sprouting leaves and shoots of things like root vegetables, young herbs and leafy greens. We’ll go into more detail about those shortly.
Why Children Should Grow Microgreens
 Microgreens are great fun and extremely easy for children to grow. Once ready, they can be used rather like salads and garnishes. They are very tasty and are extremely nutritious.
Microgreens are great fun and extremely easy for children to grow. Once ready, they can be used rather like salads and garnishes. They are very tasty and are extremely nutritious.
Because they’re so compact, they can also be grown in virtually any household. They can be grown indoors too, for example on a windowsill, so families without gardens can also enjoy growing them. What’s more, getting children to grow microgreens may save money for the household.
Growing microgreens will really educate children about nature and the importance of caring for a living thing. It’ll help them learn new skills, teach them to be responsible and also help them learn more about where food comes from.
Growing their own food may also make children more likely to try different foods, particularly natural ones like these that are so good for them. All things considered, this fun, natural, educational activity is a total win-win!
What They Are Grown In
 Microgreens are traditionally grown in shallow seed trays, which are inexpensive to buy. However, at home, they can just as easily be grown in flower pots, used yoghurt pots, empty egg cartons, the trays from ready-meals or even cut-down cardboard cores from kitchen rolls. So long as water is allowed to drain from them and they can support at least a shallow depth of compost, these can all be suitable. Plastic cartons will need a few holes punched in the bottom to allow for drainage, so parents might need to organise that in order to avoid their children hurting themselves. Other than that, it’s plain sailing for supervised children to do themselves.
Microgreens are traditionally grown in shallow seed trays, which are inexpensive to buy. However, at home, they can just as easily be grown in flower pots, used yoghurt pots, empty egg cartons, the trays from ready-meals or even cut-down cardboard cores from kitchen rolls. So long as water is allowed to drain from them and they can support at least a shallow depth of compost, these can all be suitable. Plastic cartons will need a few holes punched in the bottom to allow for drainage, so parents might need to organise that in order to avoid their children hurting themselves. Other than that, it’s plain sailing for supervised children to do themselves.
What Else is Needed?
Microgreens are usually grown from seeds and, for those, you have a couple of options. Both are very inexpensive. You can use either:
- seeds purchased in packets (e.g. from a shop or online),
- or seeds that you have saved from fully-grown herbs, fruit or vegetables. Learn more about harvesting your own seeds, potentially for free, from existing fruit, vegetables and herbs in our previous post here.
 Suitable seeds include: rocket, a type of strongly-flavoured lettuce; beetroot, with their lovely red stems and mild, earthy taste; spinach, which also has a mild flavour and is full of goodness; red cabbage, which is also rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals; fennel, which will have a distinctive aniseed flavour; broccoli, which will grow into sprouts that have a slightly spicy taste; radish seeds, which also grow into leaves that taste a little fiery; and also mustard seeds (for children who are OK with even more hot, spicy flavours).
Suitable seeds include: rocket, a type of strongly-flavoured lettuce; beetroot, with their lovely red stems and mild, earthy taste; spinach, which also has a mild flavour and is full of goodness; red cabbage, which is also rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals; fennel, which will have a distinctive aniseed flavour; broccoli, which will grow into sprouts that have a slightly spicy taste; radish seeds, which also grow into leaves that taste a little fiery; and also mustard seeds (for children who are OK with even more hot, spicy flavours).
The only other things that are needed for children to grow microgreens are water, drip trays and some compost.
- For the compost, ‘Multi-Purpose Compost’ or ‘Seed & Cuttings Compost’ are both perfect. Peat-free versions of those are even better, as they’re kinder to the environment.
- You’ll need some seed ‘drip trays’ to place under your trays or pots of microgreens. As the name suggests, these are simply trays to catch the draining water and to protect your windowsill etc. They’re inexpensive to buy but, if you’re on a budget, a saucer or suitably shaped plastic carton of some sort will be fine, so long as it’s watertight underneath and is shallow enough. This is also a great way to recycle plastic and show your child how easy it is to do so.
Setting Up & Sewing the Seeds
Setting up is easy:
 First, your child should fill the seed trays, flower pots or equivalent, almost to the top, with some compost.
First, your child should fill the seed trays, flower pots or equivalent, almost to the top, with some compost.- Then firm it down a little so it is flat and even.
- If they want to manually space out the seeds individually, then they can use a fingertip to indent where the seeds will go, then pop a seed into each indent.
- Otherwise, the fastest and easiest approach is to lightly sprinkle the seeds onto the compost. Be sure to do it lightly (tip: sprinkle from a little bit of a height to make this easier). Your child should avoid allowing the seeds to clump or be spread too densely, otherwise problems can occur once they start to grow.
- Optionally, the seeds can then be covered with a light sprinkling of more compost, just to keep them in place while still allowing some light to get to them.
- Water lightly (outside may be best to avoid any mess indoors). Be gentle when watering so the seeds do not simply wash away.
- Place the pots or trays of seeds back on the windowsill or similar. Wherever they are placed, it needs to be in full daylight during the day and also ventilated.
- Optionally, they can be temporarily covered with a piece of kitchen towel or cling film, but this is only while the seeds germinate.
- Your child should check daily to ensure that the compost stays moist. If needed, water gently from above or, if seed trays are shallow, put some water into the drip trays so the compost draws it up.
 As as shoots begin to appear (usually after just a few days), remove any covering if used and continue to ensure that the compost is always kept moist, but not over-watered.
As as shoots begin to appear (usually after just a few days), remove any covering if used and continue to ensure that the compost is always kept moist, but not over-watered.
Harvesting your Microgreens
In just one to two weeks, you should have a nice ‘blanket’ of shoots and baby leaves growing beautifully. The idea with microgreens is to harvest them while they have baby leaves, before mature leaves start to form. So, they should be harvested while still very young. Snipping them at their bases instead of pulling them up may allow them to regrow, so they can be harvested more than once.
Microgreen Meals
 Once harvested, they should be rinsed to get rid of any stray compost. They are delicious to eat and, depending on the seeds grown, have a huge variety of tastes and colours. Children and parents alike can benefit from the nutritious and tasty shoots as part of a variety of meal types. Full of vitamins and minerals, they can be used in salads, as pizza toppings, garnishes, toppings for risottos, soups and pastas, as fillings in sandwiches, sprinkled on top of baked potatoes or into burgers and much more. They’re very adaptable and, with their distinctive tastes and textures, will make any meal really special.
Once harvested, they should be rinsed to get rid of any stray compost. They are delicious to eat and, depending on the seeds grown, have a huge variety of tastes and colours. Children and parents alike can benefit from the nutritious and tasty shoots as part of a variety of meal types. Full of vitamins and minerals, they can be used in salads, as pizza toppings, garnishes, toppings for risottos, soups and pastas, as fillings in sandwiches, sprinkled on top of baked potatoes or into burgers and much more. They’re very adaptable and, with their distinctive tastes and textures, will make any meal really special.
Childcare Excellence in Streatham, SW16
 Children will love growing these little edible plants and harvesting them for food. They will learn so much along the way, building to a great sense of achievement in what is a great home learning activity. Learning at home is just as essential as all the learning that takes place at nurseries like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Children will learn best when it’s a true partnership between nurseries/pre-schools and parents, so we encourage regular feedback and cooperation.
Children will love growing these little edible plants and harvesting them for food. They will learn so much along the way, building to a great sense of achievement in what is a great home learning activity. Learning at home is just as essential as all the learning that takes place at nurseries like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Children will learn best when it’s a true partnership between nurseries/pre-schools and parents, so we encourage regular feedback and cooperation.
If you are looking for outstanding nurseries in Streatham for your baby or under-five child, please get in touch with Little Cedars Nursery. Our nursery is also near Streatham Common, Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Furzedown, Tooting, Tooting Bec, Tooting Broadway, Tooting Common, Balham, Norbury and Colliers Wood, so get in touch if you’d like to discuss or register a place for your child. We’d love to show you around …

 First, your child should fill the seed trays, flower pots or equivalent, almost to the top, with some compost.
First, your child should fill the seed trays, flower pots or equivalent, almost to the top, with some compost. As as shoots begin to appear (usually after just a few days), remove any covering if used and continue to ensure that the compost is always kept moist, but not over-watered.
As as shoots begin to appear (usually after just a few days), remove any covering if used and continue to ensure that the compost is always kept moist, but not over-watered.
 We previously covered
We previously covered  Motor dysgraphia is primarily the result of poor fine motor skills and poor dexterity, making the control needed for legible writing or drawings difficult. It may also be the result of poor muscle tone. In contrast to dyslexic dysgraphia, motor dysgraphia may result in poor writing legibility even when the words are copied. Spelling, however, is not adversely affected. Short bursts with unusually high concentration levels may result in better letter and word formation, but the level of concentration needed to achieve this is unsustainable over a longer period.
Motor dysgraphia is primarily the result of poor fine motor skills and poor dexterity, making the control needed for legible writing or drawings difficult. It may also be the result of poor muscle tone. In contrast to dyslexic dysgraphia, motor dysgraphia may result in poor writing legibility even when the words are copied. Spelling, however, is not adversely affected. Short bursts with unusually high concentration levels may result in better letter and word formation, but the level of concentration needed to achieve this is unsustainable over a longer period. sgraphic children may also hold their writing instruments in an unusual way or have strange posture when writing;
sgraphic children may also hold their writing instruments in an unusual way or have strange posture when writing; Diagnosing Dysgraphia
Diagnosing Dysgraphia At education settings, additional bespoke learning strategies and interventions, that all teaching professionals can employ, may include:
At education settings, additional bespoke learning strategies and interventions, that all teaching professionals can employ, may include: Childcare/teaching professionals and parents/guardians should always work together and compare notes, so that all parties are fully informed about any challenges the child may have. By doing so, they can share strategies and each work with the child towards the same goals. It’s important to begin such work as early as possible, so that the impact of the disorder on the child’s life is minimised. Early diagnosis is therefore crucial.
Childcare/teaching professionals and parents/guardians should always work together and compare notes, so that all parties are fully informed about any challenges the child may have. By doing so, they can share strategies and each work with the child towards the same goals. It’s important to begin such work as early as possible, so that the impact of the disorder on the child’s life is minimised. Early diagnosis is therefore crucial.
 In today’s guide, we answer frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Dyscalculia, particularly in relation to children, including preschoolers. Around 5% of children of school age are thought to have dyscalculia.
In today’s guide, we answer frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Dyscalculia, particularly in relation to children, including preschoolers. Around 5% of children of school age are thought to have dyscalculia.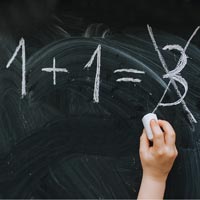 A few of the possible signs of dyscalculia include:
A few of the possible signs of dyscalculia include: They may also continue to use fingers to count long after their contemporaries have moved on to mental counting;
They may also continue to use fingers to count long after their contemporaries have moved on to mental counting; Just as with dyslexia, there is no cure for dyscalculia. However, there are many ways to help children cope with its effects. It’s also worth bearing in mind that children with dyscalculia can be very gifted in other areas, for example creativity, strategic thinking, problem solving, practical abilities and often great intuition.
Just as with dyslexia, there is no cure for dyscalculia. However, there are many ways to help children cope with its effects. It’s also worth bearing in mind that children with dyscalculia can be very gifted in other areas, for example creativity, strategic thinking, problem solving, practical abilities and often great intuition. They can also benefit when important words and numbers are highlighted (to draw attention to their importance);
They can also benefit when important words and numbers are highlighted (to draw attention to their importance);
 Your Right to Unpaid Parental Leave
Your Right to Unpaid Parental Leave For example, there may come a time when parents need to look at nurseries, pre-schools, primary and secondary schools and, as children approach their mid teens, further education settings. Other reasons to take time off might include time for parents to visit relatives with the children, or to investigate extra-curricular activities such as sports clubs, or simply to spend quality time with their children.
For example, there may come a time when parents need to look at nurseries, pre-schools, primary and secondary schools and, as children approach their mid teens, further education settings. Other reasons to take time off might include time for parents to visit relatives with the children, or to investigate extra-curricular activities such as sports clubs, or simply to spend quality time with their children. It doesn’t really matter if you change jobs. The rules around unpaid parental leave apply in relation to your child(ren); not your employer. So, if you change jobs and have already used up 9 weeks of unpaid leave for one child during your previous job, then you can still use another 9 weeks, so long as it’s taken before your child reaches the age of 18.
It doesn’t really matter if you change jobs. The rules around unpaid parental leave apply in relation to your child(ren); not your employer. So, if you change jobs and have already used up 9 weeks of unpaid leave for one child during your previous job, then you can still use another 9 weeks, so long as it’s taken before your child reaches the age of 18. To claim a period of unpaid parental leave, just 21 days (3 weeks) of notice must be given to the employer and this must state the start and finish dates. It can be confirmed verbally although employers may request the notice in writing.
To claim a period of unpaid parental leave, just 21 days (3 weeks) of notice must be given to the employer and this must state the start and finish dates. It can be confirmed verbally although employers may request the notice in writing.
 The Government’s Early Years Foundation Stage (‘EYFS’) framework prescribes how adults should approach the education and development of children under five. As such, it forms the backbone of the curriculum at childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. The EYFS guidelines were expanded this year (2021) and one aspect of early childhood development discussed therein merits closer exploration: the affect of adult interaction on an infant’s brain development. Here we take a look.
The Government’s Early Years Foundation Stage (‘EYFS’) framework prescribes how adults should approach the education and development of children under five. As such, it forms the backbone of the curriculum at childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. The EYFS guidelines were expanded this year (2021) and one aspect of early childhood development discussed therein merits closer exploration: the affect of adult interaction on an infant’s brain development. Here we take a look. Their research suggests that constructive experiences will build on and enhance the structure of the brain, whereas “adverse experiences early in life can impair brain architecture, with negative effects lasting into adulthood.”
Their research suggests that constructive experiences will build on and enhance the structure of the brain, whereas “adverse experiences early in life can impair brain architecture, with negative effects lasting into adulthood.” The Harvard Center on the Developing Child suggests that parents1 can help babies and toddlers develop their brain architecture in the best way through regular and strategic interaction between adult and infant. They call the process ‘serve and return’. Think of it as a tennis metaphor— we’ll explain. First, the child may indicate an interest in an object or activity. That’s the serve of the tennis ball, if you like. The adult should look out for such indications of interest, recognise them as a kind of invitation from the child and then get involved with that object or activity with the child. Responding in this way is like the ‘return’ of the ball in the tennis metaphor. It’s a great approach because the child is indicating what they are interested in and therefore, when a parent responds through activity involving themselves with the source of interest, the child will naturally get more from the interaction. After all, it was they who first indicated an interest and an adult can now help them to get the most from it.
The Harvard Center on the Developing Child suggests that parents1 can help babies and toddlers develop their brain architecture in the best way through regular and strategic interaction between adult and infant. They call the process ‘serve and return’. Think of it as a tennis metaphor— we’ll explain. First, the child may indicate an interest in an object or activity. That’s the serve of the tennis ball, if you like. The adult should look out for such indications of interest, recognise them as a kind of invitation from the child and then get involved with that object or activity with the child. Responding in this way is like the ‘return’ of the ball in the tennis metaphor. It’s a great approach because the child is indicating what they are interested in and therefore, when a parent responds through activity involving themselves with the source of interest, the child will naturally get more from the interaction. After all, it was they who first indicated an interest and an adult can now help them to get the most from it. Repetition is also important. This helps to reinforce circuits in the brain. Reminding a child several times about something will naturally help them to understand and remember the point under scrutiny.
Repetition is also important. This helps to reinforce circuits in the brain. Reminding a child several times about something will naturally help them to understand and remember the point under scrutiny. The research, as well as a good dose of common sense, shows the incredible importance of parents interacting well with children from the moment they are born. Their interaction and guidance will help the developing child to understand themselves, the world around them, and their place within it. Millions of brain connections are built with every interaction, building healthy foundations upon which the baby will grow into a well-rounded individual with the requisite cognitive, physical, social and emotional skills to handle life. It all comes down to love, responsive and responsible care, with parents matching the infant’s signals and needs with positive, insightful responses. The reassurance and tools such interactions give the infant will allow them to confidently, safely and comfortably explore and learn about the world and, going forwards, their place within it.
The research, as well as a good dose of common sense, shows the incredible importance of parents interacting well with children from the moment they are born. Their interaction and guidance will help the developing child to understand themselves, the world around them, and their place within it. Millions of brain connections are built with every interaction, building healthy foundations upon which the baby will grow into a well-rounded individual with the requisite cognitive, physical, social and emotional skills to handle life. It all comes down to love, responsive and responsible care, with parents matching the infant’s signals and needs with positive, insightful responses. The reassurance and tools such interactions give the infant will allow them to confidently, safely and comfortably explore and learn about the world and, going forwards, their place within it.
 3. Almost 50% More Bones Than Adults
3. Almost 50% More Bones Than Adults 6. Not So Hot on Eye Sight
6. Not So Hot on Eye Sight 9. Natural Born Swimmers (… Kind of)
9. Natural Born Swimmers (… Kind of) 14. Is Breast Really is Best?
14. Is Breast Really is Best? 16. The Only Smiling Primate
16. The Only Smiling Primate 19. Outcomes of Being First Born
19. Outcomes of Being First Born
 Following up from our
Following up from our  The father, or partner of the mother, must give their employer at least 15 weeks’ advance notice that they wish to take Statutory Paternity Leave. This can be imprecise, however, given that they won’t be 100% certain which day the child(ren) will be born. If they later change the proposed date, employers must be given at least 28 days (4 weeks) notice of the change, made in writing if requested by the employer.
The father, or partner of the mother, must give their employer at least 15 weeks’ advance notice that they wish to take Statutory Paternity Leave. This can be imprecise, however, given that they won’t be 100% certain which day the child(ren) will be born. If they later change the proposed date, employers must be given at least 28 days (4 weeks) notice of the change, made in writing if requested by the employer. the child’s father, or
the child’s father, or To be eligible for Statutory Paternity Pay, a person needs to:
To be eligible for Statutory Paternity Pay, a person needs to: The payments are made through their wages by the employer after deducting any tax and National Insurance if due. (Figures correct at September 2021).
The payments are made through their wages by the employer after deducting any tax and National Insurance if due. (Figures correct at September 2021).
 Today, we’ll take a look at how much time and money mothers are entitled to under Statutory Maternity Leave and what the eligibility requirements are. We’ll concentrate purely on the rules for mothers who are employees in this post. However, we will follow up to cover paternity leave, shared leave and support for self-employed mothers separately, in future guides.
Today, we’ll take a look at how much time and money mothers are entitled to under Statutory Maternity Leave and what the eligibility requirements are. We’ll concentrate purely on the rules for mothers who are employees in this post. However, we will follow up to cover paternity leave, shared leave and support for self-employed mothers separately, in future guides. The good news is that, to be eligible for Statutory Maternity Leave in the UK, just two main rules apply. You need to:
The good news is that, to be eligible for Statutory Maternity Leave in the UK, just two main rules apply. You need to: Statutory Maternity Pay (‘SMP’) is available to mothers who:
Statutory Maternity Pay (‘SMP’) is available to mothers who: There’s a great online tool that you can use to check whether you are eligible to claim maternity/paternity leave and pay (as well as Maternity Allowance, which may help self-employed mums). It’ll also calculate how much you could receive. Head over to
There’s a great online tool that you can use to check whether you are eligible to claim maternity/paternity leave and pay (as well as Maternity Allowance, which may help self-employed mums). It’ll also calculate how much you could receive. Head over to 
 Recent studies show that use of connected screens and devices by children, including under-fives, is growing fast. The pandemic appears to have increased kids’ screen use too, as children have spent more time indoors and less time playing ‘in person’ with friends.
Recent studies show that use of connected screens and devices by children, including under-fives, is growing fast. The pandemic appears to have increased kids’ screen use too, as children have spent more time indoors and less time playing ‘in person’ with friends. Over 75% of children under five have access to a connected device, with up to 60% of preschoolers actually owning their own.
Over 75% of children under five have access to a connected device, with up to 60% of preschoolers actually owning their own. “Parents have always played a huge role in curating what [under-fives] consume and how their time is spent, but toddlers are now confidently navigating digital platforms for themselves, and using touchscreen devices with purpose and determination.” (Childwise)
“Parents have always played a huge role in curating what [under-fives] consume and how their time is spent, but toddlers are now confidently navigating digital platforms for themselves, and using touchscreen devices with purpose and determination.” (Childwise) that the ‘RF wireless radiation’ emitted by Wi-Fi connected screens and devices may carry potential health risks particularly, they argue, for pregnant women, their unborn foetuses and the young. The very young, of course, have brains that are still at a critical development stage. For this reason, the experts concerned advocate that access to devices like mobile phones should be limited, removed from children’s bedrooms at night or, at the very least, placed in Flight Mode when possible. Using devices wired instead of using Wi-Fi apparently reduces risks. Use of them in hands-free mode is another useful approach, so that the devices are not so close to youngsters’ heads. We’re not experts ourselves, but these measures seem like sensible precautions.
that the ‘RF wireless radiation’ emitted by Wi-Fi connected screens and devices may carry potential health risks particularly, they argue, for pregnant women, their unborn foetuses and the young. The very young, of course, have brains that are still at a critical development stage. For this reason, the experts concerned advocate that access to devices like mobile phones should be limited, removed from children’s bedrooms at night or, at the very least, placed in Flight Mode when possible. Using devices wired instead of using Wi-Fi apparently reduces risks. Use of them in hands-free mode is another useful approach, so that the devices are not so close to youngsters’ heads. We’re not experts ourselves, but these measures seem like sensible precautions. While time spent by children on connected screens and devices is rising, it’s not all bad news. The pandemic has also seen an increase in the time that parents have been spending with children, including on shared screen viewing as well as on other pastimes like baking, crafts and family activities. At the end of the day, it’s all about a healthy balance and, of course, adult supervision to ensure children’s wellbeing at all times.
While time spent by children on connected screens and devices is rising, it’s not all bad news. The pandemic has also seen an increase in the time that parents have been spending with children, including on shared screen viewing as well as on other pastimes like baking, crafts and family activities. At the end of the day, it’s all about a healthy balance and, of course, adult supervision to ensure children’s wellbeing at all times.
