
You probably thinking “Brad Pitt … in Streatham?” … but bear with us! In our last post, we discovered that a Prime Minister was based in Streatham Park back in the 18th Century and Sir Henry Tate, founder of The Tate Gallery and synonymous with the Tate & Lyle sugar empire, also lived here. Continuing with our famous ‘Streathamites’ theme, we now take a look at some of the other famous, influential or important people who lived, worked, or were born in Streatham. As it turns out, it’s quite a long list with some very illustrious names — and yes — the list genuinely includes Mr Pitt! Take a look:
Famous ‘Streathamites’
 Streatham was the birthplace, home or workplace of a huge number of famous people. Just a few include:
Streatham was the birthplace, home or workplace of a huge number of famous people. Just a few include:
Sarah Beeny, the TV presenter and entrepreneur, lived for a while in Streatham before moving to Somerset.
John Torode, the co-host of MasterChef, lived in Streatham.
Simon Callow, the actor famous for films like Four Weddings & a Funeral, was born at Pinfold Road in Streatham in 1949.
 Henry Robertson Bowers, one of the explorers on the ill-fated Terra Nova exploration of the Antarctic with Robert Falcon Scott (better known as Scott of the Antarctic), lived in Streatham and attended Streatham High School for Boys in Pinfold Road.
Henry Robertson Bowers, one of the explorers on the ill-fated Terra Nova exploration of the Antarctic with Robert Falcon Scott (better known as Scott of the Antarctic), lived in Streatham and attended Streatham High School for Boys in Pinfold Road.
 Super-model Naomi Campbell was born in Streatham in 1970, the maternal daughter of a professional dancer, but never met her father.
Super-model Naomi Campbell was born in Streatham in 1970, the maternal daughter of a professional dancer, but never met her father.
 Rapper ‘Dave’ Orobosa Omeregie, also known as ‘Santan Dave’ was born in Streatham and has since scored several top-20 records and a number 1 single, as well as winning several high profile awards. One of his top ten singles was even called ‘Streatham’.
Rapper ‘Dave’ Orobosa Omeregie, also known as ‘Santan Dave’ was born in Streatham and has since scored several top-20 records and a number 1 single, as well as winning several high profile awards. One of his top ten singles was even called ‘Streatham’.
Actor Peter Davison was born and raised in Streatham, attending Granton Primary School and later, of course, becoming Doctor Who and starring in many successful films, TV productions in theatre and on radio.
 The fashion designer John Galliano lived in Streatham from the age of six, until moving later to Dulwich and subsequently other parts of London.
The fashion designer John Galliano lived in Streatham from the age of six, until moving later to Dulwich and subsequently other parts of London.
Edward Stanley Gibbons, founder of the now famous Stanley Gibbons stamp catalogue used by most philatelists, lived in later life at Stanhope Road in Streatham.
 Comedians Eddie Izzard and Paul Merton both have links to Streatham. Eddie used to host a comedy club there, in the White Lion pub. Apparently he often practised his lines when walking around Streatham Common.
Comedians Eddie Izzard and Paul Merton both have links to Streatham. Eddie used to host a comedy club there, in the White Lion pub. Apparently he often practised his lines when walking around Streatham Common.
 007 Actor Roger Moore lived in Streatham, with his then wife Doorn Van Steyn and her family, when he was just 18.
007 Actor Roger Moore lived in Streatham, with his then wife Doorn Van Steyn and her family, when he was just 18.
Those who remember TV’s Ready Steady Go from the 60s will remember one of its co-presenters, Cathy McGowan, was also from Streatham.
 Ken Livingstone was born at 21 Shrubbery Road, Streatham, in 1945 and also later attended the Philippa Fawcett Teacher Training College there. He was an MP, leader of the GLC, and later Mayor of London.
Ken Livingstone was born at 21 Shrubbery Road, Streatham, in 1945 and also later attended the Philippa Fawcett Teacher Training College there. He was an MP, leader of the GLC, and later Mayor of London.
 The actor and presenter David Harewood MBE, also lives in Streatham. He is most famous for his role as a CIA operative in the popular American series Homeland.
The actor and presenter David Harewood MBE, also lives in Streatham. He is most famous for his role as a CIA operative in the popular American series Homeland.
 Even Brad Pitt has connections to Streatham! He was filmed during a fight scene for the movie Snatch at what was then Caesar’s Nightclub at 156 Streatham Hill.
Even Brad Pitt has connections to Streatham! He was filmed during a fight scene for the movie Snatch at what was then Caesar’s Nightclub at 156 Streatham Hill.
Previously, of course, Caesar’s Nightclub was known as The Cat’s Whiskers, hosting such legendary names as Glen Miller, Laurel & Hardy, Charlie Chaplin, Rod Stewart, The Small Faces, Audrey Hepburn and The Rolling Stones. Apparently the Krays also frequented the club and Ruth Ellis, the last female to be hanged in the UK, also apparently worked there circa 1948. The venue was also the site of the first Miss World contest. Sadly the building no longer exists. It had originally been opened as The Locarno Dance Hall and was opened by Billy Cotton, the famous band leader, back in 1929. Check out the Pathé video below, which was filmed at the location in 1938.
 Speaking of The Rolling Stones, Bill Wyman, their bassist, worked for a time as a storekeeper and progress clerk. He earned £11 per week at John A. Sparks, the diesel engineers at Streatham Hill.
Speaking of The Rolling Stones, Bill Wyman, their bassist, worked for a time as a storekeeper and progress clerk. He earned £11 per week at John A. Sparks, the diesel engineers at Streatham Hill.
 June Whitfield, the actress, was born in Streatham in 1925 and later attended Streatham Hill High School.
June Whitfield, the actress, was born in Streatham in 1925 and later attended Streatham Hill High School.
The notorious madame Cynthia Payne held her infamous ‘parties’ in Streatham at 32 Ambleside Avenue.
 Famous comedian Tommy Trinder was born at 54 Wellfield Road, Streatham, in 1909. Many will remember him for his catchphrase, “You lucky people!” from the pre- and post-WW2 era.
Famous comedian Tommy Trinder was born at 54 Wellfield Road, Streatham, in 1909. Many will remember him for his catchphrase, “You lucky people!” from the pre- and post-WW2 era.
 Another former Prime Minister, John Major, also lived for a time in Streatham with his wife, Norma, at Primrose Court. He had bought the property in 1969.
Another former Prime Minister, John Major, also lived for a time in Streatham with his wife, Norma, at Primrose Court. He had bought the property in 1969.
There are many more famous people who have close links to Streatham, including more TV personalities, presenters, comedians and many important historical and military figures. We hope our snapshot above highlights just how important Streatham has been to the historical, political and cultural background of south east London and indeed to the UK as a whole. Discover more famous people from Streatham here.
Little Cedars: a Famous Nursery in Streatham!
 Are you looking for outstanding nurseries near Streatham, Streatham Common, Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Furzedown, Tooting or Balham? If so, we’d love to show you and your little one(s) around the nursery here in Aldrington Road, SW16. Places are limited for this high quality childcare setting, so please get in touch while there’s still some availability. We offer weekday childcare for babies and children up to five. Interested? Please choose a button:
Are you looking for outstanding nurseries near Streatham, Streatham Common, Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Furzedown, Tooting or Balham? If so, we’d love to show you and your little one(s) around the nursery here in Aldrington Road, SW16. Places are limited for this high quality childcare setting, so please get in touch while there’s still some availability. We offer weekday childcare for babies and children up to five. Interested? Please choose a button:
Photo Credits: Main image: by Korea.net / Korean Culture and Information Service, CC BY-SA 2.0. BP Signature on main image: reproduced by Gatoleiteiro, CC BY-SA 4.0. Simon Callow: by Ash, CC BY-SA 3.0. Henry Robertson Bowers: by Bowers, H. R. (Henry Robertson), 1883-1912, Public domain. Naomi Campbell: by Georges Biard, CC BY-SA 4.0. Santan Dave: by SamuelWren98, CC BY-SA 4.0. John Galliano: by SALLIANCE, CC BY 3.0. Eddie Izzard: by Giuseppe Sollazzo, CC BY-SA 2.0. Roger Moore: by Allan warren, CC BY-SA 3.0. Ken Livingstone: by World Economic Forum from Cologny, Switzerland, CC BY-SA 2.0. David Harewood: Red Carpet Report on Mingle Media TV, CC BY-SA 2.0. Brad Pitt (small photo): by Georges Biard, CC BY-SA 3.0. Bill Wyman: by Jacco Barth, CC BY-SA 2.0. June Whitfield: by Slapstick Festival, CC BY 2.0. Tommy Trinder: by Ministry of Information Photo Division Photographer, Public domain. John Major: Attributed to PFC Tracey L. Hall-Leahy, Public domain.








 Despite many dyslexic people being highly intelligent, dyslexia makes it difficult for them to recognise words and/or be able to break them down into their smaller components. It is recognised as a Specific Learning Difficulty (‘SpLD’) and can seriously affect their education if not recognised and addressed early.
Despite many dyslexic people being highly intelligent, dyslexia makes it difficult for them to recognise words and/or be able to break them down into their smaller components. It is recognised as a Specific Learning Difficulty (‘SpLD’) and can seriously affect their education if not recognised and addressed early. Such an affliction can have profound implications for a person. It will adversely affect their reading, writing and comprehension, thereby limiting their overall learning capability and hindering overall literacy. These are particularly critical skills during their early years as that’s at the start of their education, when the knock-on effects of such limiting factors will be at their most significant. It will slow down their progress in many topics and areas of education, also leading potentially to lower self-confidence and possibly even getting them mislabelled as ‘slow’ or ‘lazy’ by the unenlightened. Ultimately, it can severely limit their potential careers and life outcomes.
Such an affliction can have profound implications for a person. It will adversely affect their reading, writing and comprehension, thereby limiting their overall learning capability and hindering overall literacy. These are particularly critical skills during their early years as that’s at the start of their education, when the knock-on effects of such limiting factors will be at their most significant. It will slow down their progress in many topics and areas of education, also leading potentially to lower self-confidence and possibly even getting them mislabelled as ‘slow’ or ‘lazy’ by the unenlightened. Ultimately, it can severely limit their potential careers and life outcomes. Children finding it difficult to learn the alphabet;
Children finding it difficult to learn the alphabet; The child describing words and letters as visually jumbling, blurring or even moving around when they try to read them;
The child describing words and letters as visually jumbling, blurring or even moving around when they try to read them; There is no cure for dyslexia, but measures to mitigate its effects can be taken by education professionals, parents, carers and even those affected by it. It’s incredibly important, though, for both parents and education professionals to try to recognise it early, for example at nursery or pre-school, so that a suitable teaching programme can be introduced as early as possible.
There is no cure for dyslexia, but measures to mitigate its effects can be taken by education professionals, parents, carers and even those affected by it. It’s incredibly important, though, for both parents and education professionals to try to recognise it early, for example at nursery or pre-school, so that a suitable teaching programme can be introduced as early as possible.
 Teething can be an uncomfortable and painful stage for babies. As teeth start to come through, gums can become sore. Because of this, the little ones can become irritable and emotional, without really understanding why they’re feeling as they do. Every parent will know that having an irritable, tearful baby can be stressful for parents as well as for the baby. With all of this in mind, our Rough Guide to Teething should help parents to help their babies through this difficult stage.
Teething can be an uncomfortable and painful stage for babies. As teeth start to come through, gums can become sore. Because of this, the little ones can become irritable and emotional, without really understanding why they’re feeling as they do. Every parent will know that having an irritable, tearful baby can be stressful for parents as well as for the baby. With all of this in mind, our Rough Guide to Teething should help parents to help their babies through this difficult stage. Along with the bluish-grey colouration in the gums mentioned above, other signs of a teething baby include drooling, sore-looking gums, red cheeks, the baby being tearful, rubbing their ears or chewing hands/toys more than usual. If the baby does drool, ensure that their faces are regularly wiped so as to avoid painful rashes causing further discomfort.
Along with the bluish-grey colouration in the gums mentioned above, other signs of a teething baby include drooling, sore-looking gums, red cheeks, the baby being tearful, rubbing their ears or chewing hands/toys more than usual. If the baby does drool, ensure that their faces are regularly wiped so as to avoid painful rashes causing further discomfort. Once your baby has one or more teeth showing through the gum, you should start brushing their teeth right away. This typically happens at the age of about 6 months. Take a look at our
Once your baby has one or more teeth showing through the gum, you should start brushing their teeth right away. This typically happens at the age of about 6 months. Take a look at our 
 Babies benefit enormously from breast milk; from simple, practical considerations to major health benefits, many of which continue to benefit them into adulthood. Let’s take a look:
Babies benefit enormously from breast milk; from simple, practical considerations to major health benefits, many of which continue to benefit them into adulthood. Let’s take a look: Breastfeeding also has a range of significant health (and other) benefits for mothers. These include:
Breastfeeding also has a range of significant health (and other) benefits for mothers. These include: The childcare professionals at Little Cedars Nursery are keen to fall in with the wishes of parents when it comes to baby and infant milk. To that end, parents are free to supply
The childcare professionals at Little Cedars Nursery are keen to fall in with the wishes of parents when it comes to baby and infant milk. To that end, parents are free to supply 
 Also known as complementary feeding, weaning is an important milestone for any parent or baby and usually occurs when the baby reaches the age of about 6 months. Sometimes babies simply tire of milk and weaning thereby comes naturally. In other cases, a baby needs a bit more encouragement to make their transition towards solids. Here, we’ll explore the whole topic of weaning in more detail, including ways parents can help to make the transition smoothly and stress-free for all parties.
Also known as complementary feeding, weaning is an important milestone for any parent or baby and usually occurs when the baby reaches the age of about 6 months. Sometimes babies simply tire of milk and weaning thereby comes naturally. In other cases, a baby needs a bit more encouragement to make their transition towards solids. Here, we’ll explore the whole topic of weaning in more detail, including ways parents can help to make the transition smoothly and stress-free for all parties. Weaning should be fun and it’s also the only time in a child’s life where they won’t have any preconceived ideas about what foods they “do or don’t like”. So, parents can experiment, within reason of course. It’s a time when introducing new foods to the baby comes naturally once the baby has caught on to the idea of this new experience.
Weaning should be fun and it’s also the only time in a child’s life where they won’t have any preconceived ideas about what foods they “do or don’t like”. So, parents can experiment, within reason of course. It’s a time when introducing new foods to the baby comes naturally once the baby has caught on to the idea of this new experience. Don’t rush it; set aside some time with baby so it’s relaxed, otherwise everyone can get stressed, especially initially.
Don’t rush it; set aside some time with baby so it’s relaxed, otherwise everyone can get stressed, especially initially. You can later move on to whole, (adult) finger-sized pieces of very soft fruits that baby can learn to hold. However, do read the Health & Safety Considerations section below before moving to un-mashed foods.
You can later move on to whole, (adult) finger-sized pieces of very soft fruits that baby can learn to hold. However, do read the Health & Safety Considerations section below before moving to un-mashed foods. Huge care needs to be taken to avoid giving infants anything that’s going to represent a potential choking hazard. Whole grapes, cherry tomatoes or anything else of a similar size would be examples of this as they are perfectly sized to block a baby’s airway if not first chopped up. Also avoid anything hard like nuts, raw vegetables or un-mashed apple and ensure that any pips/seeds/stones are removed from fruit and bones are removed from fish or meat.
Huge care needs to be taken to avoid giving infants anything that’s going to represent a potential choking hazard. Whole grapes, cherry tomatoes or anything else of a similar size would be examples of this as they are perfectly sized to block a baby’s airway if not first chopped up. Also avoid anything hard like nuts, raw vegetables or un-mashed apple and ensure that any pips/seeds/stones are removed from fruit and bones are removed from fish or meat. Always try to maintain a varied diet for the infant, so they get all the vitamins and nutrients they need as they intake less and less milk. Ensure the foods contain sufficient iron, which can be sought from fortified cereal, fish, milk, dark green vegetables, lentils and beans. Giving them finger foods to hold and eat themselves is a great way to encourage them to feed themselves (under supervision, of course). As they grow older they can be encouraged to eat at the family table with parents/siblings and eventually upskill to using cutlery, along with eventually learning the rules around good table manners etc.
Always try to maintain a varied diet for the infant, so they get all the vitamins and nutrients they need as they intake less and less milk. Ensure the foods contain sufficient iron, which can be sought from fortified cereal, fish, milk, dark green vegetables, lentils and beans. Giving them finger foods to hold and eat themselves is a great way to encourage them to feed themselves (under supervision, of course). As they grow older they can be encouraged to eat at the family table with parents/siblings and eventually upskill to using cutlery, along with eventually learning the rules around good table manners etc.
 The EYFS framework sets the statutory approach required for pretty much every aspect of early years childcare and education provision in the UK. The standards cover the learning and development programmes, learning goals, approach to assessment, safeguarding, welfare of children, staffing, and much more. In this guide, however, we’ll focus purely on the 7 key areas of learning and development covered by the EYFS. Essentially, these form the core curriculum at nurseries like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Let’s take a look …
The EYFS framework sets the statutory approach required for pretty much every aspect of early years childcare and education provision in the UK. The standards cover the learning and development programmes, learning goals, approach to assessment, safeguarding, welfare of children, staffing, and much more. In this guide, however, we’ll focus purely on the 7 key areas of learning and development covered by the EYFS. Essentially, these form the core curriculum at nurseries like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Let’s take a look … It would be hard to overstate the importance of good communication and language skills, as they underpin early years progress in just about everything else. So, early years providers like Little Cedars encourage two-way interactions and language-rich communications between staff and children right from the outset. Childcare professionals will introduce new vocabulary regularly and help children to understand it and use it themselves through activities like story-telling, role play and question-and-answer sessions. Practitioners will regularly read with (not just to) children, using a wide variety of high quality reading materials, encouraging feedback and engagement from the children as they progress. In this way, new vocabulary is embedded, conversations come naturally and children will thrive in their language and communication skills.
It would be hard to overstate the importance of good communication and language skills, as they underpin early years progress in just about everything else. So, early years providers like Little Cedars encourage two-way interactions and language-rich communications between staff and children right from the outset. Childcare professionals will introduce new vocabulary regularly and help children to understand it and use it themselves through activities like story-telling, role play and question-and-answer sessions. Practitioners will regularly read with (not just to) children, using a wide variety of high quality reading materials, encouraging feedback and engagement from the children as they progress. In this way, new vocabulary is embedded, conversations come naturally and children will thrive in their language and communication skills. Physical development is, of course, another key skill that is foundational for children. After all, it impacts on health, mobility, strength, fitness, agility, coordination, wellbeing and general happiness. So, great care is taken at nurseries like Little Cedars to help children hone their physical skills and development incrementally, to improve all of the above. This is done through the EYFS programmes that are set and customised for each individual child. Skills like balance, gross and fine motor skills, coordination, spatial awareness, hand/eye coordination, strength and agility will therefore gradually improve and become second nature to each child as they grow. Active children will generally become more healthy children. They will also improve social skills and confidence through the activities that they participate in alongside peers. It is also, of course, great fun!
Physical development is, of course, another key skill that is foundational for children. After all, it impacts on health, mobility, strength, fitness, agility, coordination, wellbeing and general happiness. So, great care is taken at nurseries like Little Cedars to help children hone their physical skills and development incrementally, to improve all of the above. This is done through the EYFS programmes that are set and customised for each individual child. Skills like balance, gross and fine motor skills, coordination, spatial awareness, hand/eye coordination, strength and agility will therefore gradually improve and become second nature to each child as they grow. Active children will generally become more healthy children. They will also improve social skills and confidence through the activities that they participate in alongside peers. It is also, of course, great fun! Health, happiness and even the development of early years cognitive function are all underpinned by children’s personal, social and emotional development (‘PSED’). Indeed, PSED forms the backbone of children’s relationships to all adults and peers around them — and also governs how they feel they fit in. That’s all incredibly important, so childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery approach PSED as a ‘prime’ element within the EYFS curriculum. The result is that children are supported and support one another, they learn how to manage emotions and behaviours, how to eat healthy diets, look after themselves physically, and independently manage their own personal needs. All of this will have the knock-on effect of improving confidence and self-esteem and even allow them to set some of their own goals. Close bonds will be made with both staff and other children and conflicts will be more easily resolved peaceably.
Health, happiness and even the development of early years cognitive function are all underpinned by children’s personal, social and emotional development (‘PSED’). Indeed, PSED forms the backbone of children’s relationships to all adults and peers around them — and also governs how they feel they fit in. That’s all incredibly important, so childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery approach PSED as a ‘prime’ element within the EYFS curriculum. The result is that children are supported and support one another, they learn how to manage emotions and behaviours, how to eat healthy diets, look after themselves physically, and independently manage their own personal needs. All of this will have the knock-on effect of improving confidence and self-esteem and even allow them to set some of their own goals. Close bonds will be made with both staff and other children and conflicts will be more easily resolved peaceably. Reading and writing are crucial elements within every child’s education. Without these skills, learning about other topics would become much more difficult. Literacy is therefore a key area of focus within the EYFS learning and development framework. Like other nurseries, pre-schools and childcare settings that adhere to the EYFS approach, Little Cedars Nursery will therefore endeavour to encourage a love of reading within every child. Reading teaches children to comprehend language, vocabulary, grammar and spelling as well as learning more about the underlying topics themselves.
Reading and writing are crucial elements within every child’s education. Without these skills, learning about other topics would become much more difficult. Literacy is therefore a key area of focus within the EYFS learning and development framework. Like other nurseries, pre-schools and childcare settings that adhere to the EYFS approach, Little Cedars Nursery will therefore endeavour to encourage a love of reading within every child. Reading teaches children to comprehend language, vocabulary, grammar and spelling as well as learning more about the underlying topics themselves. Nurseries, pre-schools, kindergartens and other childcare settings also recognise the importance of mathematics within children’s learning and development. The EYFS curriculum caters well for this, encouraging early years professionals to help children master counting first to 10 and later to 20 and beyond. Children will learn the patterns around numbers, including recognition of odd and even numbers, along with skills like simple addition and subtraction, and the ability to recognise low quantities without having to count. They will also learn to recognise when one quantity is more than, less than or equal to another. In so doing, children will also learn the vocabulary around mathematics in readiness for school once they leave their early years setting.
Nurseries, pre-schools, kindergartens and other childcare settings also recognise the importance of mathematics within children’s learning and development. The EYFS curriculum caters well for this, encouraging early years professionals to help children master counting first to 10 and later to 20 and beyond. Children will learn the patterns around numbers, including recognition of odd and even numbers, along with skills like simple addition and subtraction, and the ability to recognise low quantities without having to count. They will also learn to recognise when one quantity is more than, less than or equal to another. In so doing, children will also learn the vocabulary around mathematics in readiness for school once they leave their early years setting. A good early years education is nothing unless children understand the world around them. The EYFS framework used by early years nurseries like Little Cedars builds in programmes to help children learn more about the world. This includes helping them to learn how to observe, recognise, describe and even draw what’s immediately around them as well as exposing them to environments like the natural world, local parks and museums. It even teaches them to recognise similarities and differences between other cultures, religions and communities in the UK and lives being lived abroad. They will get to know more about people’s roles in society too, for example through visits from police officers, firefighters and nurses. A broad range of written material (both fiction and non-fiction) will inform them further. Topics explored will touch on culture, technology, ecology, religion, community, nature and much, much more. This will enrich their knowledge and understanding of the world they live within, giving context to what they see, hear and read about as they grow older.
A good early years education is nothing unless children understand the world around them. The EYFS framework used by early years nurseries like Little Cedars builds in programmes to help children learn more about the world. This includes helping them to learn how to observe, recognise, describe and even draw what’s immediately around them as well as exposing them to environments like the natural world, local parks and museums. It even teaches them to recognise similarities and differences between other cultures, religions and communities in the UK and lives being lived abroad. They will get to know more about people’s roles in society too, for example through visits from police officers, firefighters and nurses. A broad range of written material (both fiction and non-fiction) will inform them further. Topics explored will touch on culture, technology, ecology, religion, community, nature and much, much more. This will enrich their knowledge and understanding of the world they live within, giving context to what they see, hear and read about as they grow older. Expressive arts and design are also integral elements within the EYFS curriculum. Early years childcare settings like Little Cedars ensure that children are given a wide range of opportunities to be creative and to free their imaginations. A huge variety of media, materials, tools and activities can be used by children to express themselves and communicate both visually and audibly. Colour, texture, form and function are explored along with opportunities for role play, story-telling, poetry, singing, performance and even dancing when appropriate.
Expressive arts and design are also integral elements within the EYFS curriculum. Early years childcare settings like Little Cedars ensure that children are given a wide range of opportunities to be creative and to free their imaginations. A huge variety of media, materials, tools and activities can be used by children to express themselves and communicate both visually and audibly. Colour, texture, form and function are explored along with opportunities for role play, story-telling, poetry, singing, performance and even dancing when appropriate. Little Cedars Nursery (Streatham) uses the EYFS framework to shape the educational activities and programmes that babies and children experience at the nursery. Part of this includes the setting of learning goals that each child needs to work towards as they gradually approach the age of 5, when they will move on to school. These are individual goals, tailored to the unique needs, interests, abilities – and any disabilities – of each individual child. A continuous regime of assessment will be undertaken by staff to monitor each child’s progress during their time with the nursery, with the learning programme adjusted, as necessary, along the way. A ‘Key Person’, allocated to each child, facilitates that assessment proactively. Additionally, staff will regularly engage with parents or carers/guardians to ensure that progress towards the learning and development goals is continued at home, wherever possible. Progress is communicated and a learning journal retained and available to parents at any time. In this way, each child achieves personal bests in all areas and everyone is kept up-to-date with the child’s progress.
Little Cedars Nursery (Streatham) uses the EYFS framework to shape the educational activities and programmes that babies and children experience at the nursery. Part of this includes the setting of learning goals that each child needs to work towards as they gradually approach the age of 5, when they will move on to school. These are individual goals, tailored to the unique needs, interests, abilities – and any disabilities – of each individual child. A continuous regime of assessment will be undertaken by staff to monitor each child’s progress during their time with the nursery, with the learning programme adjusted, as necessary, along the way. A ‘Key Person’, allocated to each child, facilitates that assessment proactively. Additionally, staff will regularly engage with parents or carers/guardians to ensure that progress towards the learning and development goals is continued at home, wherever possible. Progress is communicated and a learning journal retained and available to parents at any time. In this way, each child achieves personal bests in all areas and everyone is kept up-to-date with the child’s progress.
 In April last year, we published a compelling article about
In April last year, we published a compelling article about  Reading with children also makes the task less daunting, particularly for the youngest children. Reading together also makes it more interesting and more fun. When it’s more interesting and more fun, the child is going to enjoy it more and naturally want to read more often — eventually independently — and all of that is priceless as part of their education and general knowledge going forwards. Reading can also bring parent and child closer through the time spent together. It can be great fun for the adult too, particularly when the child gets older and adults are exposed to classic children’s books that perhaps they were not, themselves, exposed to when they were young.
Reading with children also makes the task less daunting, particularly for the youngest children. Reading together also makes it more interesting and more fun. When it’s more interesting and more fun, the child is going to enjoy it more and naturally want to read more often — eventually independently — and all of that is priceless as part of their education and general knowledge going forwards. Reading can also bring parent and child closer through the time spent together. It can be great fun for the adult too, particularly when the child gets older and adults are exposed to classic children’s books that perhaps they were not, themselves, exposed to when they were young. The Nuffield Foundation’s mission is to advance social wellbeing and educational opportunity. In a partnership with the University of Newcastle, the foundation funded a deep study
The Nuffield Foundation’s mission is to advance social wellbeing and educational opportunity. In a partnership with the University of Newcastle, the foundation funded a deep study It will come as no surprise, therefore, to learn that we put all of the above into practice at Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Getting closely involved in children’s reading, using a huge variety of reading material in an interactive way, gives our nursery children the very best start in life. Indeed, our childcare professionals prepare them thoroughly for school by the time they leave us. They take with them reading, writing, literacy, language, vocabulary and self-expression skills in the process — and all this accomplished at least in part through guided reading.
It will come as no surprise, therefore, to learn that we put all of the above into practice at Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Getting closely involved in children’s reading, using a huge variety of reading material in an interactive way, gives our nursery children the very best start in life. Indeed, our childcare professionals prepare them thoroughly for school by the time they leave us. They take with them reading, writing, literacy, language, vocabulary and self-expression skills in the process — and all this accomplished at least in part through guided reading.
 What are the Recommendations for Early Years Exercise?
What are the Recommendations for Early Years Exercise? What are the Benefits of Early Years Exercise?
What are the Benefits of Early Years Exercise?
 How Parents can Help
How Parents can Help Active Play & Exercise at Little Cedars Day Nursery, Streatham
Active Play & Exercise at Little Cedars Day Nursery, Streatham
 Sensory Play Ideas for Babies
Sensory Play Ideas for Babies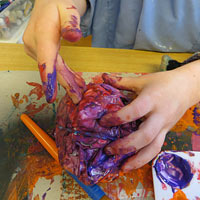 • Paper. Babies will love the feeling of scrunching up paper and will notice the sound as well as the contoured feel of their new creation. They may need a demonstration to get started, though. They’ll start to comprehend the concept that something in one form, like a pristine, wafer-thin sheet of paper, can be made into something completely different — in this case, perhaps a simple ‘ball’ of scrunched-up paper. Even
• Paper. Babies will love the feeling of scrunching up paper and will notice the sound as well as the contoured feel of their new creation. They may need a demonstration to get started, though. They’ll start to comprehend the concept that something in one form, like a pristine, wafer-thin sheet of paper, can be made into something completely different — in this case, perhaps a simple ‘ball’ of scrunched-up paper. Even  • Different objects & materials: babies will enjoy playing and learning about the properties, touch, feel and sound of different objects and materials. For example, (safe) wooden utensils, water in a closed beaker or bottle or small plastic or card boxes that they tap like a drum, or try to stack into a ‘wall’ — and so on. They’ll learn about physical properties of each along the way, including sounds, textures, touch and, if they include some carefully chosen food items, taste. It’s amazing what fun babies will have with such simple items — often learning far more from these than from purchased toys.
• Different objects & materials: babies will enjoy playing and learning about the properties, touch, feel and sound of different objects and materials. For example, (safe) wooden utensils, water in a closed beaker or bottle or small plastic or card boxes that they tap like a drum, or try to stack into a ‘wall’ — and so on. They’ll learn about physical properties of each along the way, including sounds, textures, touch and, if they include some carefully chosen food items, taste. It’s amazing what fun babies will have with such simple items — often learning far more from these than from purchased toys. • The natural world: babies also greatly enjoy the simple pleasures offered by the natural world. A breeze on their faces may greatly intrigue them, even more so when they see leaves rustling and moving a little on the ground. The feel and texture of grass on the lawn or the sight of sunlight dappling through the trees or reflecting off puddles can be wondrous to them. Under close supervision, getting to know the textures, hues and smells of safe, natural objects outdoors can also be a source of sensory discovery.
• The natural world: babies also greatly enjoy the simple pleasures offered by the natural world. A breeze on their faces may greatly intrigue them, even more so when they see leaves rustling and moving a little on the ground. The feel and texture of grass on the lawn or the sight of sunlight dappling through the trees or reflecting off puddles can be wondrous to them. Under close supervision, getting to know the textures, hues and smells of safe, natural objects outdoors can also be a source of sensory discovery.
 • Hand & foot prints: preschoolers will never be bored with smothering their hands or feet in coloured paints, then making prints on paper or card. Footprints and handprints can be random or used to make images or patterns. This process is both creative and a sensory experience for them as the cold paint squelches between fingers or toes. They’ll learn so much including about mixing pigments, creating images from simple printed shapes, about the concept of paint eventually drying to form something semi-permanent and about different textures being formed, depending on the consistency of the paint. We take these discoveries for granted as adults, but we would originally have had to learn about them during our early, formative years.
• Hand & foot prints: preschoolers will never be bored with smothering their hands or feet in coloured paints, then making prints on paper or card. Footprints and handprints can be random or used to make images or patterns. This process is both creative and a sensory experience for them as the cold paint squelches between fingers or toes. They’ll learn so much including about mixing pigments, creating images from simple printed shapes, about the concept of paint eventually drying to form something semi-permanent and about different textures being formed, depending on the consistency of the paint. We take these discoveries for granted as adults, but we would originally have had to learn about them during our early, formative years. • Food creativity: toddlers can also take playing with food to the next level by introducing the concept of making images out of things like fruit- or vegetable-based sauces, cream or yogurt. Whole pictures can be made of food, using the hands, for example using broccoli for ‘trees’, peas for grassy areas and so on. The whole thing can smell great and even be tasted! Playing, hands-on, with food in this way can be fun and creative but also help children learn to accept new foods and tastes into their diets. However, care needs to be taken because proper mealtimes require good manners and children need to understand that food is not usually for playing with.
• Food creativity: toddlers can also take playing with food to the next level by introducing the concept of making images out of things like fruit- or vegetable-based sauces, cream or yogurt. Whole pictures can be made of food, using the hands, for example using broccoli for ‘trees’, peas for grassy areas and so on. The whole thing can smell great and even be tasted! Playing, hands-on, with food in this way can be fun and creative but also help children learn to accept new foods and tastes into their diets. However, care needs to be taken because proper mealtimes require good manners and children need to understand that food is not usually for playing with. • Sensory sand: it’s very rare for little ones to dislike playing with sand, which allows youngsters to get hands-on creatively. They can learn about the unique and varying textures, consistencies and properties of sand, depending on how much moisture it contains. Dry sand has its own unique set of properties, acting and feeling almost like a powder. Very runny, wet sand is great fun as it can be used to run through the hands and ‘set’ into pointy mountain shapes that look quite magical. Or, when less water is added, sand can be fashioned into shapes and, of course, “castles”, using the hands or by filling buckets, hollow vessels, or tubs. Children can also press their hands and feet into level, damp sand in a sandpit or tray, to make impressions and patterns. It feels great too and is an almost essential part of childhood. Young children learn so much from this stimulating, multi-sensory type of play.
• Sensory sand: it’s very rare for little ones to dislike playing with sand, which allows youngsters to get hands-on creatively. They can learn about the unique and varying textures, consistencies and properties of sand, depending on how much moisture it contains. Dry sand has its own unique set of properties, acting and feeling almost like a powder. Very runny, wet sand is great fun as it can be used to run through the hands and ‘set’ into pointy mountain shapes that look quite magical. Or, when less water is added, sand can be fashioned into shapes and, of course, “castles”, using the hands or by filling buckets, hollow vessels, or tubs. Children can also press their hands and feet into level, damp sand in a sandpit or tray, to make impressions and patterns. It feels great too and is an almost essential part of childhood. Young children learn so much from this stimulating, multi-sensory type of play. • Playing with dough: whether bought or home-made, dough is always a big hit with young children. It can be fashioned with the hands into shapes, characters, animals and mini-sculptures. Using food colouring in dough also allows children to discover more about mixing pigments. Salt dough can also be baked (under the close supervision of an adult) so that it hardens into more permanent creations. Many types of dough even smell great too! What’s more, it can even lead to a bigger interest in cooking real, edible dough and other baked foods when they’re a little older.
• Playing with dough: whether bought or home-made, dough is always a big hit with young children. It can be fashioned with the hands into shapes, characters, animals and mini-sculptures. Using food colouring in dough also allows children to discover more about mixing pigments. Salt dough can also be baked (under the close supervision of an adult) so that it hardens into more permanent creations. Many types of dough even smell great too! What’s more, it can even lead to a bigger interest in cooking real, edible dough and other baked foods when they’re a little older. • A sensory garden. We’ve left perhaps the best until last. Making a sensory garden area with, or for, little ones will give them a magical experience. There are so many materials that can be used in the construction of sensory gardens, including soil, earth, pea shingle, tree bark, moss and so on. Plants themselves will also add to the fascinating mixture of textures, colours and even smells found within a sensory garden. It can be as small or large as you have room for and can even be achieved in containers, pots or on balconies for those who do not have gardens. It can take many forms so it’s design also gives children a wonderful creative opportunity. Sensory gardens are a complete feast for the senses for young children — adults too — encompassing touch (e.g. the textures of materials, moss and plants), smell (why not include some herbs — these smell wonderful and can be tasted too), potentially sound (crunchy gravel, rustling leaves etc.), sight (aesthetics, colour etc.) and will also give children ample opportunity to improve balance and body awareness as they construct and create in this unique space.
• A sensory garden. We’ve left perhaps the best until last. Making a sensory garden area with, or for, little ones will give them a magical experience. There are so many materials that can be used in the construction of sensory gardens, including soil, earth, pea shingle, tree bark, moss and so on. Plants themselves will also add to the fascinating mixture of textures, colours and even smells found within a sensory garden. It can be as small or large as you have room for and can even be achieved in containers, pots or on balconies for those who do not have gardens. It can take many forms so it’s design also gives children a wonderful creative opportunity. Sensory gardens are a complete feast for the senses for young children — adults too — encompassing touch (e.g. the textures of materials, moss and plants), smell (why not include some herbs — these smell wonderful and can be tasted too), potentially sound (crunchy gravel, rustling leaves etc.), sight (aesthetics, colour etc.) and will also give children ample opportunity to improve balance and body awareness as they construct and create in this unique space.