
 In a follow-up to last month’s post about transitioning under-fives to nursery or pre-school, we now outline 20 ways parents can help prepare children for starting school as they approach the age of five. We’ve broken this down into a list of 20 easy-to-action suggestions:
In a follow-up to last month’s post about transitioning under-fives to nursery or pre-school, we now outline 20 ways parents can help prepare children for starting school as they approach the age of five. We’ve broken this down into a list of 20 easy-to-action suggestions:
1. A Good Early Years Education
Our absolute topmost tip is to ensure that children attend a good nursery/pre-school well before the age of five. Study after study has shown that a good early years education gives little ones a massive head start in terms of school readiness, with long-term benefits continuing even into adulthood.
2. Help Learning at Home
 Parental involvement with children’s early years education has also been shown to boost achievement, morale, attitude, behaviour and social skills enormously. These are all things that will help them to hit the ground running once they start school. Home learning is even more powerful when designed to synchronise with what children are learning at their early years setting or school (like a two-pronged approach).
Parental involvement with children’s early years education has also been shown to boost achievement, morale, attitude, behaviour and social skills enormously. These are all things that will help them to hit the ground running once they start school. Home learning is even more powerful when designed to synchronise with what children are learning at their early years setting or school (like a two-pronged approach).
3. Read With Them
 Reading with children, well ahead of them beginning school, has also been shown to boost their language skills, incredibly by the equivalent of as much as 8 months before they’re even five! The key is to read with them; not just to them. Learn more about the benefits of reading with under-fives here.
Reading with children, well ahead of them beginning school, has also been shown to boost their language skills, incredibly by the equivalent of as much as 8 months before they’re even five! The key is to read with them; not just to them. Learn more about the benefits of reading with under-fives here.
4. Forewarn Them
Forewarning children that they will be starting school around the age of five is also a sensible thing to do. It should be mentioned multiple times before they reach the age of five, so children learn to expect and accept it. Just treat it as normal (which, of course, it is to you and I) and be enthusiastic about it.
5. Listen Up
 Listen to any reservations your child may have about the prospect of starting school. Listening is important, so be on the look-out for any concerns and reservations they may have.
Listen to any reservations your child may have about the prospect of starting school. Listening is important, so be on the look-out for any concerns and reservations they may have.
6. Answer Questions
Try to read between the lines too, as they may not be able to fully articulate everything they’re feeling at such a young age. Answer any questions they may have about school and take time to ensure they understand the answers.
7. Reassure Them
At all times reassure children when discussing anything about starting school and life there once they’ve started. Put their minds at rest. Focus on the positives. Mention the many benefits of school, so they look forward to it rather than getting anxious about it. After all, it’s fun, educational, they will make lots of new friends and there will be lots of new equipment to play with — and so on. You can also mention your own positive memories of school so that they know you’ve been through it yourself.
8. Encourage Independence
 Children will greatly benefit in Reception Year at school if they’re already independent when they start. So, nurturing aspects of their independence well ahead of them beginning school is a good policy. For example, ensuring they know how to independently look after personal hygiene, dress themselves, tie shoe laces, dress, use the toilet, pack their bag and so on. If they can do this before they start school, it will help them enormously.
Children will greatly benefit in Reception Year at school if they’re already independent when they start. So, nurturing aspects of their independence well ahead of them beginning school is a good policy. For example, ensuring they know how to independently look after personal hygiene, dress themselves, tie shoe laces, dress, use the toilet, pack their bag and so on. If they can do this before they start school, it will help them enormously.
9. Encourage Social Skills
Social skills are another thing to nurture in children well before they begin school. Communication skills will help them to get on. Good manners, politeness and knowing right from wrong will also help them fit in, make friends and be positively viewed from the ‘get go’.
10. Identify A Friend
 Parents/guardians will also be wise to identify one or more of their children’s friends (or potential friends) that will also be starting school at the same time. Ensure they meet up and play regularly, before they’ve started school. In this way, there will be a friendly face at the school from the moment they start. It’ll help them feel more at home and less alone.
Parents/guardians will also be wise to identify one or more of their children’s friends (or potential friends) that will also be starting school at the same time. Ensure they meet up and play regularly, before they’ve started school. In this way, there will be a friendly face at the school from the moment they start. It’ll help them feel more at home and less alone.
11. Show Them a Prospectus/Brochure/Website
It’s also a wise idea for children to acquaint themselves as much as possible with their new school, before they actually start. Therefore, obtaining a prospectus, brochure and/or taking a good look at the school’s website together would be an excellent idea for children. It’ll really help them to know what to expect.
12. Visit Ahead of Starting
Even better is a physical visit. Schools will offer open days or one can usually be arranged for children and their parents. Having a tour will help children get to know their way around the school, see the facilities, ask questions and bring the school into much clearer focus for the child. It’ll make it more tangible and less of a daunting prospect for the child if they already know it. Seeing the facilities and equipment may even excite them.
13. Pre-Sync Children’s Body Clocks
 Several weeks before they start school, children should start to synchronise their day with the timings of the new school day. This should include getting up time in the morning and ideally even timings for lunch and suchlike. In this way, children’s body clocks will have adjusted in good time, before they actually start.
Several weeks before they start school, children should start to synchronise their day with the timings of the new school day. This should include getting up time in the morning and ideally even timings for lunch and suchlike. In this way, children’s body clocks will have adjusted in good time, before they actually start.
14. Ensure They Get Enough Sleep
Getting enough sleep is critically important for children. After all, they do not want to end up struggling to stay awake during their school lessons. Therefore setting a sensible bedtime — and sticking to it — is crucially important. A gradual wind-down towards bedtime will help them sleep well as will the avoidance of electronic screens in the run-up to bedtime.
15. Prepare Their Uniform/Clothing
 Ensuring children have everything they need, at least a little ahead of starting in Reception, is a good approach. Check that you have all items of their uniform, PE kit, any stationery, lunch box if appropriate, backpack or bag and so on. Is everything marked with your child’s name? Usually it should be.
Ensuring children have everything they need, at least a little ahead of starting in Reception, is a good approach. Check that you have all items of their uniform, PE kit, any stationery, lunch box if appropriate, backpack or bag and so on. Is everything marked with your child’s name? Usually it should be.
16. Do a Dummy School Run
Close to the time the child will start at their new school, it is a good idea for parents/guardians to do a dummy run to the school at the actual times the child will eventually be dropped off and picked up. In this way, parents/guardians can ensure that they won’t be late, which might otherwise cause more stress for both themselves and their child. It’s important for the first day, in particular, to be as stress-free as possible.
17. Help Them to Pre-Pack
Getting your child involved in actually packing their backpack or school bag (with supervision) will help them to acquaint themselves with everything in it. That way, if they need something when they’re at school, they’ll know they have it and where they can find it. Doing this the night before, with the exception of food if it needs to be kept refrigerated overnight, will mean there’s also less to do on Day One.
18. Be on Time On the Day
All this pre-planning should make it more likely that you’re on time at the school on the first day. That’s important, as a last-minute rush will only cause unnecessary stress for both you and your little one. So, ensure you leave for the journey in good time. And don’t be late at picking-up time!
19. Reassure & Don’t Fuss on the Day
If you’re anxious, stressed or sad on your child’s first day, don’t let on. It’s best to keep everything positive as far as your child is concerned. So, stay up-beat, calm and reassuring. As we said before, focus on the positives (“you’re going to have so much fun!” etc.) and it will all seem so much more ‘normal’ for your child — as normal as a walk in the park.
20. Ensure They Know Who Will Collect Them
 Your child will need to know, ahead of time, who is collecting them. If it’s not you, then they need to know clearly who it will be. They also need to be clear around their general safety rules, stranger danger and so on. Schools should also have safeguarding policies in place for unexpected scenarios. For example, if you are unexpectedly delayed and need to send someone else to collect your child, does the school have a password system in place to ensure that only the right person can collect your child? Find out.
Your child will need to know, ahead of time, who is collecting them. If it’s not you, then they need to know clearly who it will be. They also need to be clear around their general safety rules, stranger danger and so on. Schools should also have safeguarding policies in place for unexpected scenarios. For example, if you are unexpectedly delayed and need to send someone else to collect your child, does the school have a password system in place to ensure that only the right person can collect your child? Find out.
Also, as a parent, you’ll need to ensure you have the requisite contact details for any relevant school personnel (e.g. the number of the main office/reception desk) in case you need to contact them for any reason. They must also have your number and any back-up contact details.
A Good Early Years Education at Little Cedars Nursery & Pre-school, Streatham
 Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham offers babies, toddlers and under-fives a really good early years education as part of its high quality childcare service. If you are looking for the best nurseries or pre-schools in the Streatham area, Little Cedars Nursery really should be on your short list. Children absolutely thrive at the setting, achieving personal bests in every area of the early years curriculum and becoming ‘ school ready’ by the time they leave us to move on to Reception at school. We offer outstandingly good childcare services in Streatham, near Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Streatham Common and Furzedown and are convenient for those living or working in Tooting, Tooting Bec, Tooting Broadway, Tooting Common, Balham, Norbury and Colliers Wood. To arrange a visit, ask any questions or to apply for a place, please get in contact — simply choose a button below.
Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham offers babies, toddlers and under-fives a really good early years education as part of its high quality childcare service. If you are looking for the best nurseries or pre-schools in the Streatham area, Little Cedars Nursery really should be on your short list. Children absolutely thrive at the setting, achieving personal bests in every area of the early years curriculum and becoming ‘ school ready’ by the time they leave us to move on to Reception at school. We offer outstandingly good childcare services in Streatham, near Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Streatham Common and Furzedown and are convenient for those living or working in Tooting, Tooting Bec, Tooting Broadway, Tooting Common, Balham, Norbury and Colliers Wood. To arrange a visit, ask any questions or to apply for a place, please get in contact — simply choose a button below.


 Whether or not you’ve finished
Whether or not you’ve finished  In the weeks or even months before their first day, toddlers and preschoolers will also benefit from becoming more independent. You can help to encourage this. For example, you could help them with toilet training, help them learn to dress themselves, encourage them to deal with personal hygiene, cleaning their hands and so on. Can they pack their own backpack? Do they know how to hang their coat up? Helping them to master all such skills will make them more confident and relaxed once they begin at nursery/pre-school.
In the weeks or even months before their first day, toddlers and preschoolers will also benefit from becoming more independent. You can help to encourage this. For example, you could help them with toilet training, help them learn to dress themselves, encourage them to deal with personal hygiene, cleaning their hands and so on. Can they pack their own backpack? Do they know how to hang their coat up? Helping them to master all such skills will make them more confident and relaxed once they begin at nursery/pre-school. Any good nursery or pre-school will be more than willing to show you and your child around the setting — more than once if required. At Little Cedars Nursery, this is commonplace and it gives parents and children the opportunity to see the setting actually ‘in action’. They can ask questions, see all the amazing facilities, equipment and toys, speak to the childcare professionals and see if they feel at home. Settling-in sessions are also an option, prior to fully joining.
Any good nursery or pre-school will be more than willing to show you and your child around the setting — more than once if required. At Little Cedars Nursery, this is commonplace and it gives parents and children the opportunity to see the setting actually ‘in action’. They can ask questions, see all the amazing facilities, equipment and toys, speak to the childcare professionals and see if they feel at home. Settling-in sessions are also an option, prior to fully joining. Such sessions and visits are also a great way for children to get to know other children at the setting, or even to discover that an existing friend already attends. Knowing someone who will be at the same nursery or pre-school will help them settle straight in, being a friendly face to greet them from the moment they start. Getting to know the childcare practitioners ahead of starting is also going to help, of course, so they feel at home, secure and looked after by someone familiar, right from the word go.
Such sessions and visits are also a great way for children to get to know other children at the setting, or even to discover that an existing friend already attends. Knowing someone who will be at the same nursery or pre-school will help them settle straight in, being a friendly face to greet them from the moment they start. Getting to know the childcare practitioners ahead of starting is also going to help, of course, so they feel at home, secure and looked after by someone familiar, right from the word go. Being fully prepared is a big part of the success of this important milestone. However, there are a few things parent/carers can do for children on the actual day they start nursery or pre-school.
Being fully prepared is a big part of the success of this important milestone. However, there are a few things parent/carers can do for children on the actual day they start nursery or pre-school. When you drop your child off, don’t make too much of a fuss about being apart from your child. Also, remind them that you’ll be seeing them later when it’s time for them to come home again. This will all reassure them. And, if you can, see if you can pair them up with a friend for them to go in with. Chances are, they’ll then hardly be able to contain themselves with excitement and will not even look back!
When you drop your child off, don’t make too much of a fuss about being apart from your child. Also, remind them that you’ll be seeing them later when it’s time for them to come home again. This will all reassure them. And, if you can, see if you can pair them up with a friend for them to go in with. Chances are, they’ll then hardly be able to contain themselves with excitement and will not even look back!
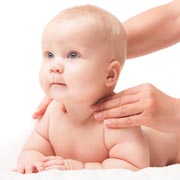 Welcome to our quick guide to Tummy Time. One of the most important things for babies during their earliest development is to build strength, muscles, motor skills and coordination. In particular, learning to lift and safely move their heads is one of the most crucial skills at this young age. Strength and muscle coordination in their neck is therefore very important. That’s not easy when they’re newborns in their first few weeks because their head is comparatively large and heavy compared with their little bodies at that age. Building upper body strength in arms, shoulders, core and back will also greatly help them in their physical development and mobility, essentially helping them to perform and survive safely as humans. Tummy Time is a key tool in learning to accomplish all of these goals — and many more.
Welcome to our quick guide to Tummy Time. One of the most important things for babies during their earliest development is to build strength, muscles, motor skills and coordination. In particular, learning to lift and safely move their heads is one of the most crucial skills at this young age. Strength and muscle coordination in their neck is therefore very important. That’s not easy when they’re newborns in their first few weeks because their head is comparatively large and heavy compared with their little bodies at that age. Building upper body strength in arms, shoulders, core and back will also greatly help them in their physical development and mobility, essentially helping them to perform and survive safely as humans. Tummy Time is a key tool in learning to accomplish all of these goals — and many more. What is Tummy Time?
What is Tummy Time? It helps to stop the development of deformations in the skull. ‘Positional plagiocephaly’ (or ‘Flat Head Syndrome’) might otherwise occur if the baby is only positioned in a limited number of positions, i.e. mostly on its back. Bear in mind, of course, that at this young age the baby’s skull bones are far more flexible than those of an adult, so such deformations are more likely if the baby’s head is always lying in the same position.
It helps to stop the development of deformations in the skull. ‘Positional plagiocephaly’ (or ‘Flat Head Syndrome’) might otherwise occur if the baby is only positioned in a limited number of positions, i.e. mostly on its back. Bear in mind, of course, that at this young age the baby’s skull bones are far more flexible than those of an adult, so such deformations are more likely if the baby’s head is always lying in the same position. Making sense of sensory stimuli is also aided by the positive results of Tummy Time, as babies can better explore and gain improved sensory perception of everything in their immediate vicinity.
Making sense of sensory stimuli is also aided by the positive results of Tummy Time, as babies can better explore and gain improved sensory perception of everything in their immediate vicinity. Try putting the baby in a prone position (i.e. on their tummy) on, say, a clean blanket or rug. Lie down on your tummy too and face them, encouraging them to stay on their tummies by use of a game like peek-a-boo. If you can, try to get them to raise themselves onto their arms or, eventually, hands. Move yourself around a little, so they move too and strengthen their muscles. If they’re finding it too difficult initially, a rolled-up blanket underneath their chest may help to start them off. Don’t worry if at first they can only push themselves up on their arms or hands only for fleeting moments; they will gradually improve as they try more and more.
Try putting the baby in a prone position (i.e. on their tummy) on, say, a clean blanket or rug. Lie down on your tummy too and face them, encouraging them to stay on their tummies by use of a game like peek-a-boo. If you can, try to get them to raise themselves onto their arms or, eventually, hands. Move yourself around a little, so they move too and strengthen their muscles. If they’re finding it too difficult initially, a rolled-up blanket underneath their chest may help to start them off. Don’t worry if at first they can only push themselves up on their arms or hands only for fleeting moments; they will gradually improve as they try more and more.
 After 6 months, they should start to be able to support their weight on their arms in a raised, kind of ‘press-up’ position. This can be encouraged with some support (and play) from you and they’ll get the hang of it with practise. Soon enough, they’ll also be able to roll sideways in either direction and get themselves back into the prone position when they want to. They’ll soon master the art of passing a toy from one hand to another at around this time. They’ll also be able to get themselves into a sitting position before they’re 9 months old, or thereabouts.
After 6 months, they should start to be able to support their weight on their arms in a raised, kind of ‘press-up’ position. This can be encouraged with some support (and play) from you and they’ll get the hang of it with practise. Soon enough, they’ll also be able to roll sideways in either direction and get themselves back into the prone position when they want to. They’ll soon master the art of passing a toy from one hand to another at around this time. They’ll also be able to get themselves into a sitting position before they’re 9 months old, or thereabouts.
 Let’s first take a look at the benefits of vegetarianism …
Let’s first take a look at the benefits of vegetarianism … is linked to a reduction in symptoms for those with asthma;
is linked to a reduction in symptoms for those with asthma; Scientific studies conclude that switching to a vegetarian diet will help the planet enormously. That’s because significantly less greenhouse gas is produced in growing crops compared to raising livestock. What’s more, scientists believe that the necessary reduction in green house gas emissions will be achieved far more swiftly through a widespread switch to vegetarianism than through what’s currently just a gradual shift away from the burning of fossil fuels. Growing crops rather than animals also causes far less pollution in waterways and oceans and also uses significantly less water. The benefits of vegetarianism to the planet are simply enormous.
Scientific studies conclude that switching to a vegetarian diet will help the planet enormously. That’s because significantly less greenhouse gas is produced in growing crops compared to raising livestock. What’s more, scientists believe that the necessary reduction in green house gas emissions will be achieved far more swiftly through a widespread switch to vegetarianism than through what’s currently just a gradual shift away from the burning of fossil fuels. Growing crops rather than animals also causes far less pollution in waterways and oceans and also uses significantly less water. The benefits of vegetarianism to the planet are simply enormous. Is a Vegetarian or Vegan Diet Safe for Children?
Is a Vegetarian or Vegan Diet Safe for Children?

 Back in April last year, we wrote an article about
Back in April last year, we wrote an article about  Microgreens are great fun and extremely easy for children to grow. Once ready, they can be used rather like salads and garnishes. They are very tasty and are extremely nutritious.
Microgreens are great fun and extremely easy for children to grow. Once ready, they can be used rather like salads and garnishes. They are very tasty and are extremely nutritious. Microgreens are traditionally grown in shallow seed trays, which are inexpensive to buy. However, at home, they can just as easily be grown in flower pots, used yoghurt pots, empty egg cartons, the trays from ready-meals or even cut-down cardboard cores from kitchen rolls. So long as water is allowed to drain from them and they can support at least a shallow depth of compost, these can all be suitable. Plastic cartons will need a few holes punched in the bottom to allow for drainage, so parents might need to organise that in order to avoid their children hurting themselves. Other than that, it’s plain sailing for supervised children to do themselves.
Microgreens are traditionally grown in shallow seed trays, which are inexpensive to buy. However, at home, they can just as easily be grown in flower pots, used yoghurt pots, empty egg cartons, the trays from ready-meals or even cut-down cardboard cores from kitchen rolls. So long as water is allowed to drain from them and they can support at least a shallow depth of compost, these can all be suitable. Plastic cartons will need a few holes punched in the bottom to allow for drainage, so parents might need to organise that in order to avoid their children hurting themselves. Other than that, it’s plain sailing for supervised children to do themselves. Suitable seeds include: rocket, a type of strongly-flavoured lettuce; beetroot, with their lovely red stems and mild, earthy taste; spinach, which also has a mild flavour and is full of goodness; red cabbage, which is also rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals; fennel, which will have a distinctive aniseed flavour; broccoli, which will grow into sprouts that have a slightly spicy taste; radish seeds, which also grow into leaves that taste a little fiery; and also mustard seeds (for children who are OK with even more hot, spicy flavours).
Suitable seeds include: rocket, a type of strongly-flavoured lettuce; beetroot, with their lovely red stems and mild, earthy taste; spinach, which also has a mild flavour and is full of goodness; red cabbage, which is also rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals; fennel, which will have a distinctive aniseed flavour; broccoli, which will grow into sprouts that have a slightly spicy taste; radish seeds, which also grow into leaves that taste a little fiery; and also mustard seeds (for children who are OK with even more hot, spicy flavours). First, your child should fill the seed trays, flower pots or equivalent, almost to the top, with some compost.
First, your child should fill the seed trays, flower pots or equivalent, almost to the top, with some compost. As as shoots begin to appear (usually after just a few days), remove any covering if used and continue to ensure that the compost is always kept moist, but not over-watered.
As as shoots begin to appear (usually after just a few days), remove any covering if used and continue to ensure that the compost is always kept moist, but not over-watered. Once harvested, they should be rinsed to get rid of any stray compost. They are delicious to eat and, depending on the seeds grown, have a huge variety of tastes and colours. Children and parents alike can benefit from the nutritious and tasty shoots as part of a variety of meal types. Full of vitamins and minerals, they can be used in salads, as pizza toppings, garnishes, toppings for risottos, soups and pastas, as fillings in sandwiches, sprinkled on top of baked potatoes or into burgers and much more. They’re very adaptable and, with their distinctive tastes and textures, will make any meal really special.
Once harvested, they should be rinsed to get rid of any stray compost. They are delicious to eat and, depending on the seeds grown, have a huge variety of tastes and colours. Children and parents alike can benefit from the nutritious and tasty shoots as part of a variety of meal types. Full of vitamins and minerals, they can be used in salads, as pizza toppings, garnishes, toppings for risottos, soups and pastas, as fillings in sandwiches, sprinkled on top of baked potatoes or into burgers and much more. They’re very adaptable and, with their distinctive tastes and textures, will make any meal really special.
 We previously covered
We previously covered  Motor dysgraphia is primarily the result of poor fine motor skills and poor dexterity, making the control needed for legible writing or drawings difficult. It may also be the result of poor muscle tone. In contrast to dyslexic dysgraphia, motor dysgraphia may result in poor writing legibility even when the words are copied. Spelling, however, is not adversely affected. Short bursts with unusually high concentration levels may result in better letter and word formation, but the level of concentration needed to achieve this is unsustainable over a longer period.
Motor dysgraphia is primarily the result of poor fine motor skills and poor dexterity, making the control needed for legible writing or drawings difficult. It may also be the result of poor muscle tone. In contrast to dyslexic dysgraphia, motor dysgraphia may result in poor writing legibility even when the words are copied. Spelling, however, is not adversely affected. Short bursts with unusually high concentration levels may result in better letter and word formation, but the level of concentration needed to achieve this is unsustainable over a longer period. sgraphic children may also hold their writing instruments in an unusual way or have strange posture when writing;
sgraphic children may also hold their writing instruments in an unusual way or have strange posture when writing; Diagnosing Dysgraphia
Diagnosing Dysgraphia At education settings, additional bespoke learning strategies and interventions, that all teaching professionals can employ, may include:
At education settings, additional bespoke learning strategies and interventions, that all teaching professionals can employ, may include: Childcare/teaching professionals and parents/guardians should always work together and compare notes, so that all parties are fully informed about any challenges the child may have. By doing so, they can share strategies and each work with the child towards the same goals. It’s important to begin such work as early as possible, so that the impact of the disorder on the child’s life is minimised. Early diagnosis is therefore crucial.
Childcare/teaching professionals and parents/guardians should always work together and compare notes, so that all parties are fully informed about any challenges the child may have. By doing so, they can share strategies and each work with the child towards the same goals. It’s important to begin such work as early as possible, so that the impact of the disorder on the child’s life is minimised. Early diagnosis is therefore crucial.
 In today’s guide, we answer frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Dyscalculia, particularly in relation to children, including preschoolers. Around 5% of children of school age are thought to have dyscalculia.
In today’s guide, we answer frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Dyscalculia, particularly in relation to children, including preschoolers. Around 5% of children of school age are thought to have dyscalculia. A few of the possible signs of dyscalculia include:
A few of the possible signs of dyscalculia include: They may also continue to use fingers to count long after their contemporaries have moved on to mental counting;
They may also continue to use fingers to count long after their contemporaries have moved on to mental counting; Just as with dyslexia, there is no cure for dyscalculia. However, there are many ways to help children cope with its effects. It’s also worth bearing in mind that children with dyscalculia can be very gifted in other areas, for example creativity, strategic thinking, problem solving, practical abilities and often great intuition.
Just as with dyslexia, there is no cure for dyscalculia. However, there are many ways to help children cope with its effects. It’s also worth bearing in mind that children with dyscalculia can be very gifted in other areas, for example creativity, strategic thinking, problem solving, practical abilities and often great intuition. They can also benefit when important words and numbers are highlighted (to draw attention to their importance);
They can also benefit when important words and numbers are highlighted (to draw attention to their importance);
 The Government’s Early Years Foundation Stage (‘EYFS’) framework prescribes how adults should approach the education and development of children under five. As such, it forms the backbone of the curriculum at childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. The EYFS guidelines were expanded this year (2021) and one aspect of early childhood development discussed therein merits closer exploration: the affect of adult interaction on an infant’s brain development. Here we take a look.
The Government’s Early Years Foundation Stage (‘EYFS’) framework prescribes how adults should approach the education and development of children under five. As such, it forms the backbone of the curriculum at childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. The EYFS guidelines were expanded this year (2021) and one aspect of early childhood development discussed therein merits closer exploration: the affect of adult interaction on an infant’s brain development. Here we take a look. Their research suggests that constructive experiences will build on and enhance the structure of the brain, whereas “adverse experiences early in life can impair brain architecture, with negative effects lasting into adulthood.”
Their research suggests that constructive experiences will build on and enhance the structure of the brain, whereas “adverse experiences early in life can impair brain architecture, with negative effects lasting into adulthood.” The Harvard Center on the Developing Child suggests that parents1 can help babies and toddlers develop their brain architecture in the best way through regular and strategic interaction between adult and infant. They call the process ‘serve and return’. Think of it as a tennis metaphor— we’ll explain. First, the child may indicate an interest in an object or activity. That’s the serve of the tennis ball, if you like. The adult should look out for such indications of interest, recognise them as a kind of invitation from the child and then get involved with that object or activity with the child. Responding in this way is like the ‘return’ of the ball in the tennis metaphor. It’s a great approach because the child is indicating what they are interested in and therefore, when a parent responds through activity involving themselves with the source of interest, the child will naturally get more from the interaction. After all, it was they who first indicated an interest and an adult can now help them to get the most from it.
The Harvard Center on the Developing Child suggests that parents1 can help babies and toddlers develop their brain architecture in the best way through regular and strategic interaction between adult and infant. They call the process ‘serve and return’. Think of it as a tennis metaphor— we’ll explain. First, the child may indicate an interest in an object or activity. That’s the serve of the tennis ball, if you like. The adult should look out for such indications of interest, recognise them as a kind of invitation from the child and then get involved with that object or activity with the child. Responding in this way is like the ‘return’ of the ball in the tennis metaphor. It’s a great approach because the child is indicating what they are interested in and therefore, when a parent responds through activity involving themselves with the source of interest, the child will naturally get more from the interaction. After all, it was they who first indicated an interest and an adult can now help them to get the most from it. Repetition is also important. This helps to reinforce circuits in the brain. Reminding a child several times about something will naturally help them to understand and remember the point under scrutiny.
Repetition is also important. This helps to reinforce circuits in the brain. Reminding a child several times about something will naturally help them to understand and remember the point under scrutiny. The research, as well as a good dose of common sense, shows the incredible importance of parents interacting well with children from the moment they are born. Their interaction and guidance will help the developing child to understand themselves, the world around them, and their place within it. Millions of brain connections are built with every interaction, building healthy foundations upon which the baby will grow into a well-rounded individual with the requisite cognitive, physical, social and emotional skills to handle life. It all comes down to love, responsive and responsible care, with parents matching the infant’s signals and needs with positive, insightful responses. The reassurance and tools such interactions give the infant will allow them to confidently, safely and comfortably explore and learn about the world and, going forwards, their place within it.
The research, as well as a good dose of common sense, shows the incredible importance of parents interacting well with children from the moment they are born. Their interaction and guidance will help the developing child to understand themselves, the world around them, and their place within it. Millions of brain connections are built with every interaction, building healthy foundations upon which the baby will grow into a well-rounded individual with the requisite cognitive, physical, social and emotional skills to handle life. It all comes down to love, responsive and responsible care, with parents matching the infant’s signals and needs with positive, insightful responses. The reassurance and tools such interactions give the infant will allow them to confidently, safely and comfortably explore and learn about the world and, going forwards, their place within it.
 3. Almost 50% More Bones Than Adults
3. Almost 50% More Bones Than Adults 6. Not So Hot on Eye Sight
6. Not So Hot on Eye Sight 9. Natural Born Swimmers (… Kind of)
9. Natural Born Swimmers (… Kind of) 14. Is Breast Really is Best?
14. Is Breast Really is Best? 16. The Only Smiling Primate
16. The Only Smiling Primate 19. Outcomes of Being First Born
19. Outcomes of Being First Born