
 Once babies can crawl, they’re well on their way to becoming toddlers. Then, in no time at all, they can suddenly become fully mobile, able to climb and even be out of your sight in just seconds. With this new mobility comes exploration, the potential for danger and even possible injury. With that in mind, we bring you 20 ways to begin childproofing your home to keep little ones safer and further from harm’s way.
Once babies can crawl, they’re well on their way to becoming toddlers. Then, in no time at all, they can suddenly become fully mobile, able to climb and even be out of your sight in just seconds. With this new mobility comes exploration, the potential for danger and even possible injury. With that in mind, we bring you 20 ways to begin childproofing your home to keep little ones safer and further from harm’s way.
1. Safety Gates
 Safety gates, strategically placed around the home, are a great way to keep your little one confined to a safer, controlled area. There are lots of different types available, whether new or second-hand, but make sure they’re made to UK safety standards. Some are suitable for doorways and others for stairs. Using safety gates to keep young children away from stairs, kitchens and other hazardous places really is a no-brainer and a great place to start with your childproofing exercise.
Safety gates, strategically placed around the home, are a great way to keep your little one confined to a safer, controlled area. There are lots of different types available, whether new or second-hand, but make sure they’re made to UK safety standards. Some are suitable for doorways and others for stairs. Using safety gates to keep young children away from stairs, kitchens and other hazardous places really is a no-brainer and a great place to start with your childproofing exercise.
2. Clear Glass Safety
 Clear floor-to-ceiling glass is also a hazard once children are mobile. Therefore such glass, whether part of a window, patio door, glass partition or conservatory should ideally not be clear all the way down. Otherwise, an unsuspecting child — or even adult — could find themselves running straight through what they thought was an opening. An easy way to ensure glass can be seen as a barrier is to use strategically placed stickers dotted around on the glass. These could be fun and attractive, for example little flower or butterfly stickers. Alternatively, you can even buy modern-looking ‘frosting’ strips that, when applied in one or more horizontal stripes or shapes at an appropriate height, will make clear glass more visible to you and your child. Guards are, of course, another possible temporary option.
Clear floor-to-ceiling glass is also a hazard once children are mobile. Therefore such glass, whether part of a window, patio door, glass partition or conservatory should ideally not be clear all the way down. Otherwise, an unsuspecting child — or even adult — could find themselves running straight through what they thought was an opening. An easy way to ensure glass can be seen as a barrier is to use strategically placed stickers dotted around on the glass. These could be fun and attractive, for example little flower or butterfly stickers. Alternatively, you can even buy modern-looking ‘frosting’ strips that, when applied in one or more horizontal stripes or shapes at an appropriate height, will make clear glass more visible to you and your child. Guards are, of course, another possible temporary option.
3. Cupboard Security
 Whether they’re in the kitchen, on the landing, under the stairs or elsewhere, cupboards can represent a number of possible hazards to children. Fingers can be hurt if shut in the doors or near the hinges and the cupboards themselves can contain any number of dangerous things. Therefore, it’s wise to obtain some childproof locks, latches or catches for cupboard doors that you don’t want your child to be able to open. These are often simple, easy to affix (and remove when children are older) and can be inexpensive if you shop around.
Whether they’re in the kitchen, on the landing, under the stairs or elsewhere, cupboards can represent a number of possible hazards to children. Fingers can be hurt if shut in the doors or near the hinges and the cupboards themselves can contain any number of dangerous things. Therefore, it’s wise to obtain some childproof locks, latches or catches for cupboard doors that you don’t want your child to be able to open. These are often simple, easy to affix (and remove when children are older) and can be inexpensive if you shop around.
4. Window & Door Security
 Similarly, ensure that entrance/exit doors throughout your home are secure where they need to be. Front doors, doors to gardens, balconies and patios all need to be particularly well secured from access by young children, whether through locks, latches or specialist childproofing mechanisms (there are lots available on the market). Similarly, windows need to be secure and that’s never more true than when there’s a nasty drop the other side.
Similarly, ensure that entrance/exit doors throughout your home are secure where they need to be. Front doors, doors to gardens, balconies and patios all need to be particularly well secured from access by young children, whether through locks, latches or specialist childproofing mechanisms (there are lots available on the market). Similarly, windows need to be secure and that’s never more true than when there’s a nasty drop the other side.
5. Door Stops & Wedges
Door stops and door wedges are a simple and inexpensive way to make doors safer to little ones. With children’s fingers small enough to get into hinges, under doors or to be potentially shut in them when they close, door stops, door wedges and ‘finger guards’ are a complete no-brainer and are quick and easy to affix.
6. Hazardous Machines & Gizmos
 Everything with a motor or moving parts is a potential hazard to small children. The obvious items to keep well beyond their reach are tools like drills and saws along with household appliances like vacuums, food mixers and coffee-makers. However, larger things like washing machines, tumble driers, dishwashers and any appliance with a door that they could climb into are also potentially very dangerous for little ones. It may even take a combination of precautions to keep children safe from such hazards.
Everything with a motor or moving parts is a potential hazard to small children. The obvious items to keep well beyond their reach are tools like drills and saws along with household appliances like vacuums, food mixers and coffee-makers. However, larger things like washing machines, tumble driers, dishwashers and any appliance with a door that they could climb into are also potentially very dangerous for little ones. It may even take a combination of precautions to keep children safe from such hazards.
7. Hazardous Products
 Another reason to keep little ones out of cupboards and certain areas of the home is to keep them safe from hazardous products. Some things will be poisonous and others may be corrosive. Dishwasher and laundry pods need to be stored well out of children’s reach as do medicines, cleaning products and DIY items like paint, solvents and glues. Any of these could prove fatal if they get into little hands. Remember, too, that children learn to climb, so even cupboards high up need to be secured.
Another reason to keep little ones out of cupboards and certain areas of the home is to keep them safe from hazardous products. Some things will be poisonous and others may be corrosive. Dishwasher and laundry pods need to be stored well out of children’s reach as do medicines, cleaning products and DIY items like paint, solvents and glues. Any of these could prove fatal if they get into little hands. Remember, too, that children learn to climb, so even cupboards high up need to be secured.
8. Smoke Alarms
 Smoke alarms suitably located around the home are one of the most basic precautions any parent or carer can make. Countless lives are saved each year due to smoke alarms. Sadly, though, many are also lost due to them not being present or due to batteries having expired. So, ensure that smoke alarms are ideally in every room as well as being in hallways, stairwells and so on. Also test them regularly to ensure batteries are in good, working order.
Smoke alarms suitably located around the home are one of the most basic precautions any parent or carer can make. Countless lives are saved each year due to smoke alarms. Sadly, though, many are also lost due to them not being present or due to batteries having expired. So, ensure that smoke alarms are ideally in every room as well as being in hallways, stairwells and so on. Also test them regularly to ensure batteries are in good, working order.
9. Carbon Monoxide Alarms
It’s the same with carbon monoxide alarms although you usually need less of them (it’s best to follow instructions when you’ve purchased them). Carbon monoxide is a silent killer as it can’t be seen or smelt. Detectors are therefore wise in homes that have a heater or heating system, even if it’s in an adjoining garage or property (gas can travel). Remember to check and test batteries too, of course.
10. Electric Point ‘Protector’ Inserts — Good or Bad?
Electrical shocks are nasty, even when a household has circuit-breakers (as indeed they should). Therefore, many might assume that plastic socket ‘blanking’ inserts would be a wise addition to electrical outlets around the home, particularly as they are often located within easy reach of little fingers. Nowadays in the UK, however, power socket blanking inserts have become controversial and indeed the Department of Health has condemned their use due to safety concerns. More information about the dangers of socket inserts can be read in the Department of Health’s safety alert here. Ofsted, meanwhile, does not offer any specific guidance on the topic. Children also need to be educated generally about electrical hazards, of course, keeping away from power points, avoiding yanking out plugs, keeping water away from power sources and so on.
11. Wire Tidiness
 For similar reasons, it’s also wise to keep electrical wire cords tidy and out of reach of little ones. If they were to pull a kettle lead or trip over an electric iron lead, for example, the potential outcomes do not bear thinking about. Cords on telephones and electrical appliances are also choking hazards, of course. So, keep them out of harm’s way i.e. well out of grabbing and tripping distance.
For similar reasons, it’s also wise to keep electrical wire cords tidy and out of reach of little ones. If they were to pull a kettle lead or trip over an electric iron lead, for example, the potential outcomes do not bear thinking about. Cords on telephones and electrical appliances are also choking hazards, of course. So, keep them out of harm’s way i.e. well out of grabbing and tripping distance.
12. Pull Cord Precautions
 Dangling pull-cords on window blinds have, regrettably, been the cause of several deaths around the world. If they’re dangling down, small children could get these wrapped around their necks and potentially strangle themselves. Any toggle on the end of the cords can also be a choking hazard. So, if you have any of these in your home, ensure they are tied safely out of reach, ideally using the safety fitments that often come with new blinds, or are available inexpensively. The same kind of approach may also be needed in rooms where the electrical light, shower or extractor switch comes in a pull-cord form.
Dangling pull-cords on window blinds have, regrettably, been the cause of several deaths around the world. If they’re dangling down, small children could get these wrapped around their necks and potentially strangle themselves. Any toggle on the end of the cords can also be a choking hazard. So, if you have any of these in your home, ensure they are tied safely out of reach, ideally using the safety fitments that often come with new blinds, or are available inexpensively. The same kind of approach may also be needed in rooms where the electrical light, shower or extractor switch comes in a pull-cord form.
13. Heated Appliances
 Heat sources are a terrible hazard for children and adults alike. However, little ones will seldom realise the hazards, so parents and guardians need to ensure that all heat sources are kept well out of children’s reach. Examples include hair straighteners, irons, kettles, sandwich makers, pots and pans that have been on the cooker, and so on. With regard to cookers, hobs, grills, and ovens, it’s the children that need to be kept away from them, of course. Even a switched-off oven can still have a door that’s retained enough heat to burn little hands. A combination of several of the precautions outlined in this page may therefore help to make complete safety feasible in the kitchen and anywhere there are appliances that heat up.
Heat sources are a terrible hazard for children and adults alike. However, little ones will seldom realise the hazards, so parents and guardians need to ensure that all heat sources are kept well out of children’s reach. Examples include hair straighteners, irons, kettles, sandwich makers, pots and pans that have been on the cooker, and so on. With regard to cookers, hobs, grills, and ovens, it’s the children that need to be kept away from them, of course. Even a switched-off oven can still have a door that’s retained enough heat to burn little hands. A combination of several of the precautions outlined in this page may therefore help to make complete safety feasible in the kitchen and anywhere there are appliances that heat up.
14. Home Heating
 Radiators, heaters and, of course, fires, stoves and any other heat source in fireplaces are terribly dangerous things for children. Therefore radiator covers, fire guards, permanent vigilance and a good dose of common sense should enable parents and carers to keep children well away from such heat sources.
Radiators, heaters and, of course, fires, stoves and any other heat source in fireplaces are terribly dangerous things for children. Therefore radiator covers, fire guards, permanent vigilance and a good dose of common sense should enable parents and carers to keep children well away from such heat sources.
15. Sharp Objects
Similarly, supervising adults must ensure that all sharp objects are well out of reach of little hands.  Scissors, knives, razors, needles, hand tools like saws and screwdrivers must be locked well away and never left lying around. Even pens and pencils are sharp and dangerous around eyes, when you think about it. So, it’s imperative that parents/guardians are vigilant and supervise at all times when it comes to anything sharp or pointed.
Scissors, knives, razors, needles, hand tools like saws and screwdrivers must be locked well away and never left lying around. Even pens and pencils are sharp and dangerous around eyes, when you think about it. So, it’s imperative that parents/guardians are vigilant and supervise at all times when it comes to anything sharp or pointed.
16. Sharp Corners
Corners and edges of furniture or household equipment can be nasty things for children to bang themselves against, particularly corners of things like stone coffee tables or timber units. You wouldn’t want to fall and bang your head against a corner like that! Luckily, it’s possible to purchase ‘bumper covers’ (a.k.a. ‘bumpers’) that can pad hard edges and corners such as these. Then, if the worst happens, at least the child is protected. Vigilance will still be needed, however, as bumpers can only go so far.
Vigilance will still be needed, however, as bumpers can only go so far.
17. Choking Hazards
Choking on small objects is, of course, a common worry for parents of the very youngest children. Anything that’s small enough to block an airway, or to make a child choke, should be tidied away to somewhere they can’t access it.
18. Tablecloths
 Table cloths and table runners may look attractive but are another hazard around children, albeit a less obvious one. They look innocuous enough, but should a child grab one end and walk or fall way, they could end up with all sorts of things crashing upon them. When you think about what goes on tables (e.g. glassware, candles, china etc.), this could potentially be disastrous. So, the best advice is to completely avoid their use around young children and certainly never to allow any edges to hang down at ‘grabbing’ height.
Table cloths and table runners may look attractive but are another hazard around children, albeit a less obvious one. They look innocuous enough, but should a child grab one end and walk or fall way, they could end up with all sorts of things crashing upon them. When you think about what goes on tables (e.g. glassware, candles, china etc.), this could potentially be disastrous. So, the best advice is to completely avoid their use around young children and certainly never to allow any edges to hang down at ‘grabbing’ height.
19. The Not-Always-So-Great Outdoors
 Supervised access to the garden or other outdoor space or environment is good for even the youngest of children. However, they must never be allowed to just wander into the garden or street unaccompanied (of course). There are countless dangers outside, including poisonous plants, stranger danger, cars and many other hazards. Even in your own garden there are usually hazards, from steps, inclines and level drops to dangerous garden tools plus another type of hazard we’ll see in our last tip below. Therefore exit points in the property need to be secure (see tip #4 above) and supervised at all times around the very young.
Supervised access to the garden or other outdoor space or environment is good for even the youngest of children. However, they must never be allowed to just wander into the garden or street unaccompanied (of course). There are countless dangers outside, including poisonous plants, stranger danger, cars and many other hazards. Even in your own garden there are usually hazards, from steps, inclines and level drops to dangerous garden tools plus another type of hazard we’ll see in our last tip below. Therefore exit points in the property need to be secure (see tip #4 above) and supervised at all times around the very young.
20. Water Hazards
 Gardens often have ponds or, if you’re lucky enough, hot tubs and even swimming pools. These are all hazards to young children. Even a puddle is a potential drowning hazard to the very young. It’s the same indoors, with baths and even basins of water being potential drowning hazards. So, once again, parents and any supervising adults need to be doing just that, i.e. supervising anywhere there is water. For different reasons, that’s even more the case around hot water, of course, and anywhere a child could potentially splash or pour water near electrics.
Gardens often have ponds or, if you’re lucky enough, hot tubs and even swimming pools. These are all hazards to young children. Even a puddle is a potential drowning hazard to the very young. It’s the same indoors, with baths and even basins of water being potential drowning hazards. So, once again, parents and any supervising adults need to be doing just that, i.e. supervising anywhere there is water. For different reasons, that’s even more the case around hot water, of course, and anywhere a child could potentially splash or pour water near electrics.
So, the main requirements for the safety of children are a continuous risk assessment, installing measures to reduce any risks identified, plus vigilance and supervision around young children at all times.
Little Cedars Nursery & Pre-school: an Outstanding Childcare Service in Streatham
Our Nursery is in Streatham, close to Furzedown, Tooting, Balham, Norbury & Colliers Wood
 Are you searching for the best nurseries or pre-schools in the Streatham area? Little Cedars is a wonderful nursery/pre-school offering an outstanding weekday childcare service for babies and children under-five. Our childcare setting is also very near to Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Streatham Common, Furzedown, Tooting, Tooting Bec, Tooting Broadway, Tooting Common, Balham, Norbury and Colliers Wood, so may also suit you if you live or work in any of those London locations.
Are you searching for the best nurseries or pre-schools in the Streatham area? Little Cedars is a wonderful nursery/pre-school offering an outstanding weekday childcare service for babies and children under-five. Our childcare setting is also very near to Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Streatham Common, Furzedown, Tooting, Tooting Bec, Tooting Broadway, Tooting Common, Balham, Norbury and Colliers Wood, so may also suit you if you live or work in any of those London locations.
If you’d like to apply for a place for your child, arrange a preliminary tour, or simply ask us a question, please get in touch. We’ll be delighted to help — please simply choose a button:
Safety Notice
The ideas above are only a starting point. Every parent, carer or guardian is advised to methodically risk assess their home and any environment their child is likely to gain access to — and to take the appropriate safety precautions for their own particular child and situation.


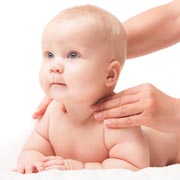 Welcome to our quick guide to Tummy Time. One of the most important things for babies during their earliest development is to build strength, muscles, motor skills and coordination. In particular, learning to lift and safely move their heads is one of the most crucial skills at this young age. Strength and muscle coordination in their neck is therefore very important. That’s not easy when they’re newborns in their first few weeks because their head is comparatively large and heavy compared with their little bodies at that age. Building upper body strength in arms, shoulders, core and back will also greatly help them in their physical development and mobility, essentially helping them to perform and survive safely as humans. Tummy Time is a key tool in learning to accomplish all of these goals — and many more.
Welcome to our quick guide to Tummy Time. One of the most important things for babies during their earliest development is to build strength, muscles, motor skills and coordination. In particular, learning to lift and safely move their heads is one of the most crucial skills at this young age. Strength and muscle coordination in their neck is therefore very important. That’s not easy when they’re newborns in their first few weeks because their head is comparatively large and heavy compared with their little bodies at that age. Building upper body strength in arms, shoulders, core and back will also greatly help them in their physical development and mobility, essentially helping them to perform and survive safely as humans. Tummy Time is a key tool in learning to accomplish all of these goals — and many more. What is Tummy Time?
What is Tummy Time? It helps to stop the development of deformations in the skull. ‘Positional plagiocephaly’ (or ‘Flat Head Syndrome’) might otherwise occur if the baby is only positioned in a limited number of positions, i.e. mostly on its back. Bear in mind, of course, that at this young age the baby’s skull bones are far more flexible than those of an adult, so such deformations are more likely if the baby’s head is always lying in the same position.
It helps to stop the development of deformations in the skull. ‘Positional plagiocephaly’ (or ‘Flat Head Syndrome’) might otherwise occur if the baby is only positioned in a limited number of positions, i.e. mostly on its back. Bear in mind, of course, that at this young age the baby’s skull bones are far more flexible than those of an adult, so such deformations are more likely if the baby’s head is always lying in the same position. Making sense of sensory stimuli is also aided by the positive results of Tummy Time, as babies can better explore and gain improved sensory perception of everything in their immediate vicinity.
Making sense of sensory stimuli is also aided by the positive results of Tummy Time, as babies can better explore and gain improved sensory perception of everything in their immediate vicinity. Try putting the baby in a prone position (i.e. on their tummy) on, say, a clean blanket or rug. Lie down on your tummy too and face them, encouraging them to stay on their tummies by use of a game like peek-a-boo. If you can, try to get them to raise themselves onto their arms or, eventually, hands. Move yourself around a little, so they move too and strengthen their muscles. If they’re finding it too difficult initially, a rolled-up blanket underneath their chest may help to start them off. Don’t worry if at first they can only push themselves up on their arms or hands only for fleeting moments; they will gradually improve as they try more and more.
Try putting the baby in a prone position (i.e. on their tummy) on, say, a clean blanket or rug. Lie down on your tummy too and face them, encouraging them to stay on their tummies by use of a game like peek-a-boo. If you can, try to get them to raise themselves onto their arms or, eventually, hands. Move yourself around a little, so they move too and strengthen their muscles. If they’re finding it too difficult initially, a rolled-up blanket underneath their chest may help to start them off. Don’t worry if at first they can only push themselves up on their arms or hands only for fleeting moments; they will gradually improve as they try more and more.
 After 6 months, they should start to be able to support their weight on their arms in a raised, kind of ‘press-up’ position. This can be encouraged with some support (and play) from you and they’ll get the hang of it with practise. Soon enough, they’ll also be able to roll sideways in either direction and get themselves back into the prone position when they want to. They’ll soon master the art of passing a toy from one hand to another at around this time. They’ll also be able to get themselves into a sitting position before they’re 9 months old, or thereabouts.
After 6 months, they should start to be able to support their weight on their arms in a raised, kind of ‘press-up’ position. This can be encouraged with some support (and play) from you and they’ll get the hang of it with practise. Soon enough, they’ll also be able to roll sideways in either direction and get themselves back into the prone position when they want to. They’ll soon master the art of passing a toy from one hand to another at around this time. They’ll also be able to get themselves into a sitting position before they’re 9 months old, or thereabouts.
 Back in April last year, we wrote an article about
Back in April last year, we wrote an article about  Microgreens are great fun and extremely easy for children to grow. Once ready, they can be used rather like salads and garnishes. They are very tasty and are extremely nutritious.
Microgreens are great fun and extremely easy for children to grow. Once ready, they can be used rather like salads and garnishes. They are very tasty and are extremely nutritious. Microgreens are traditionally grown in shallow seed trays, which are inexpensive to buy. However, at home, they can just as easily be grown in flower pots, used yoghurt pots, empty egg cartons, the trays from ready-meals or even cut-down cardboard cores from kitchen rolls. So long as water is allowed to drain from them and they can support at least a shallow depth of compost, these can all be suitable. Plastic cartons will need a few holes punched in the bottom to allow for drainage, so parents might need to organise that in order to avoid their children hurting themselves. Other than that, it’s plain sailing for supervised children to do themselves.
Microgreens are traditionally grown in shallow seed trays, which are inexpensive to buy. However, at home, they can just as easily be grown in flower pots, used yoghurt pots, empty egg cartons, the trays from ready-meals or even cut-down cardboard cores from kitchen rolls. So long as water is allowed to drain from them and they can support at least a shallow depth of compost, these can all be suitable. Plastic cartons will need a few holes punched in the bottom to allow for drainage, so parents might need to organise that in order to avoid their children hurting themselves. Other than that, it’s plain sailing for supervised children to do themselves. Suitable seeds include: rocket, a type of strongly-flavoured lettuce; beetroot, with their lovely red stems and mild, earthy taste; spinach, which also has a mild flavour and is full of goodness; red cabbage, which is also rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals; fennel, which will have a distinctive aniseed flavour; broccoli, which will grow into sprouts that have a slightly spicy taste; radish seeds, which also grow into leaves that taste a little fiery; and also mustard seeds (for children who are OK with even more hot, spicy flavours).
Suitable seeds include: rocket, a type of strongly-flavoured lettuce; beetroot, with their lovely red stems and mild, earthy taste; spinach, which also has a mild flavour and is full of goodness; red cabbage, which is also rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals; fennel, which will have a distinctive aniseed flavour; broccoli, which will grow into sprouts that have a slightly spicy taste; radish seeds, which also grow into leaves that taste a little fiery; and also mustard seeds (for children who are OK with even more hot, spicy flavours). First, your child should fill the seed trays, flower pots or equivalent, almost to the top, with some compost.
First, your child should fill the seed trays, flower pots or equivalent, almost to the top, with some compost. As as shoots begin to appear (usually after just a few days), remove any covering if used and continue to ensure that the compost is always kept moist, but not over-watered.
As as shoots begin to appear (usually after just a few days), remove any covering if used and continue to ensure that the compost is always kept moist, but not over-watered. Once harvested, they should be rinsed to get rid of any stray compost. They are delicious to eat and, depending on the seeds grown, have a huge variety of tastes and colours. Children and parents alike can benefit from the nutritious and tasty shoots as part of a variety of meal types. Full of vitamins and minerals, they can be used in salads, as pizza toppings, garnishes, toppings for risottos, soups and pastas, as fillings in sandwiches, sprinkled on top of baked potatoes or into burgers and much more. They’re very adaptable and, with their distinctive tastes and textures, will make any meal really special.
Once harvested, they should be rinsed to get rid of any stray compost. They are delicious to eat and, depending on the seeds grown, have a huge variety of tastes and colours. Children and parents alike can benefit from the nutritious and tasty shoots as part of a variety of meal types. Full of vitamins and minerals, they can be used in salads, as pizza toppings, garnishes, toppings for risottos, soups and pastas, as fillings in sandwiches, sprinkled on top of baked potatoes or into burgers and much more. They’re very adaptable and, with their distinctive tastes and textures, will make any meal really special. Children will love growing these little edible plants and harvesting them for food. They will learn so much along the way, building to a great sense of achievement in what is a great home learning activity. Learning at home is just as essential as all the learning that takes place at nurseries like
Children will love growing these little edible plants and harvesting them for food. They will learn so much along the way, building to a great sense of achievement in what is a great home learning activity. Learning at home is just as essential as all the learning that takes place at nurseries like 
 The Government’s Early Years Foundation Stage (‘EYFS’) framework prescribes how adults should approach the education and development of children under five. As such, it forms the backbone of the curriculum at childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. The EYFS guidelines were expanded this year (2021) and one aspect of early childhood development discussed therein merits closer exploration: the affect of adult interaction on an infant’s brain development. Here we take a look.
The Government’s Early Years Foundation Stage (‘EYFS’) framework prescribes how adults should approach the education and development of children under five. As such, it forms the backbone of the curriculum at childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. The EYFS guidelines were expanded this year (2021) and one aspect of early childhood development discussed therein merits closer exploration: the affect of adult interaction on an infant’s brain development. Here we take a look. Their research suggests that constructive experiences will build on and enhance the structure of the brain, whereas “adverse experiences early in life can impair brain architecture, with negative effects lasting into adulthood.”
Their research suggests that constructive experiences will build on and enhance the structure of the brain, whereas “adverse experiences early in life can impair brain architecture, with negative effects lasting into adulthood.” The Harvard Center on the Developing Child suggests that parents1 can help babies and toddlers develop their brain architecture in the best way through regular and strategic interaction between adult and infant. They call the process ‘serve and return’. Think of it as a tennis metaphor— we’ll explain. First, the child may indicate an interest in an object or activity. That’s the serve of the tennis ball, if you like. The adult should look out for such indications of interest, recognise them as a kind of invitation from the child and then get involved with that object or activity with the child. Responding in this way is like the ‘return’ of the ball in the tennis metaphor. It’s a great approach because the child is indicating what they are interested in and therefore, when a parent responds through activity involving themselves with the source of interest, the child will naturally get more from the interaction. After all, it was they who first indicated an interest and an adult can now help them to get the most from it.
The Harvard Center on the Developing Child suggests that parents1 can help babies and toddlers develop their brain architecture in the best way through regular and strategic interaction between adult and infant. They call the process ‘serve and return’. Think of it as a tennis metaphor— we’ll explain. First, the child may indicate an interest in an object or activity. That’s the serve of the tennis ball, if you like. The adult should look out for such indications of interest, recognise them as a kind of invitation from the child and then get involved with that object or activity with the child. Responding in this way is like the ‘return’ of the ball in the tennis metaphor. It’s a great approach because the child is indicating what they are interested in and therefore, when a parent responds through activity involving themselves with the source of interest, the child will naturally get more from the interaction. After all, it was they who first indicated an interest and an adult can now help them to get the most from it. Repetition is also important. This helps to reinforce circuits in the brain. Reminding a child several times about something will naturally help them to understand and remember the point under scrutiny.
Repetition is also important. This helps to reinforce circuits in the brain. Reminding a child several times about something will naturally help them to understand and remember the point under scrutiny. The research, as well as a good dose of common sense, shows the incredible importance of parents interacting well with children from the moment they are born. Their interaction and guidance will help the developing child to understand themselves, the world around them, and their place within it. Millions of brain connections are built with every interaction, building healthy foundations upon which the baby will grow into a well-rounded individual with the requisite cognitive, physical, social and emotional skills to handle life. It all comes down to love, responsive and responsible care, with parents matching the infant’s signals and needs with positive, insightful responses. The reassurance and tools such interactions give the infant will allow them to confidently, safely and comfortably explore and learn about the world and, going forwards, their place within it.
The research, as well as a good dose of common sense, shows the incredible importance of parents interacting well with children from the moment they are born. Their interaction and guidance will help the developing child to understand themselves, the world around them, and their place within it. Millions of brain connections are built with every interaction, building healthy foundations upon which the baby will grow into a well-rounded individual with the requisite cognitive, physical, social and emotional skills to handle life. It all comes down to love, responsive and responsible care, with parents matching the infant’s signals and needs with positive, insightful responses. The reassurance and tools such interactions give the infant will allow them to confidently, safely and comfortably explore and learn about the world and, going forwards, their place within it.
 3. Almost 50% More Bones Than Adults
3. Almost 50% More Bones Than Adults 6. Not So Hot on Eye Sight
6. Not So Hot on Eye Sight 9. Natural Born Swimmers (… Kind of)
9. Natural Born Swimmers (… Kind of) 14. Is Breast Really is Best?
14. Is Breast Really is Best? 16. The Only Smiling Primate
16. The Only Smiling Primate 19. Outcomes of Being First Born
19. Outcomes of Being First Born
 Being let loose with coloured paints, art materials and creative opportunities is sure to bring a smile to their faces and a sense of enormous fun, creativity and discovery. No doubt too; they’ll be proud to show others their creations!
Being let loose with coloured paints, art materials and creative opportunities is sure to bring a smile to their faces and a sense of enormous fun, creativity and discovery. No doubt too; they’ll be proud to show others their creations! As well as being enormous fun, messy play allows children to express themselves in unbounded creative ways. That’s important. Self-expression and creativity will help children to gain a sense of achievement and, through this subtle way, a greater sense of self-worth and confidence.
As well as being enormous fun, messy play allows children to express themselves in unbounded creative ways. That’s important. Self-expression and creativity will help children to gain a sense of achievement and, through this subtle way, a greater sense of self-worth and confidence. Hand-eye coordination will also benefit, of course.
Hand-eye coordination will also benefit, of course. We fully understand the many benefits of messy play at Little Cedars Nursery, of course. Indeed, it’s part of the curriculum. Under-fives are encouraged to learn through messy play using an enormous wealth of resources, equipment and materials at the setting. That’s both indoors and in our outside play areas. From paint and paper indoors to sandpits and water play outside, toddlers and preschoolers have a wonderful time with messy play at Little Cedars, all in a safe, structured, fun and educational environment.
We fully understand the many benefits of messy play at Little Cedars Nursery, of course. Indeed, it’s part of the curriculum. Under-fives are encouraged to learn through messy play using an enormous wealth of resources, equipment and materials at the setting. That’s both indoors and in our outside play areas. From paint and paper indoors to sandpits and water play outside, toddlers and preschoolers have a wonderful time with messy play at Little Cedars, all in a safe, structured, fun and educational environment.
 Recent studies show that use of connected screens and devices by children, including under-fives, is growing fast. The pandemic appears to have increased kids’ screen use too, as children have spent more time indoors and less time playing ‘in person’ with friends.
Recent studies show that use of connected screens and devices by children, including under-fives, is growing fast. The pandemic appears to have increased kids’ screen use too, as children have spent more time indoors and less time playing ‘in person’ with friends. Over 75% of children under five have access to a connected device, with up to 60% of preschoolers actually owning their own.
Over 75% of children under five have access to a connected device, with up to 60% of preschoolers actually owning their own. “Parents have always played a huge role in curating what [under-fives] consume and how their time is spent, but toddlers are now confidently navigating digital platforms for themselves, and using touchscreen devices with purpose and determination.” (Childwise)
“Parents have always played a huge role in curating what [under-fives] consume and how their time is spent, but toddlers are now confidently navigating digital platforms for themselves, and using touchscreen devices with purpose and determination.” (Childwise) that the ‘RF wireless radiation’ emitted by Wi-Fi connected screens and devices may carry potential health risks particularly, they argue, for pregnant women, their unborn foetuses and the young. The very young, of course, have brains that are still at a critical development stage. For this reason, the experts concerned advocate that access to devices like mobile phones should be limited, removed from children’s bedrooms at night or, at the very least, placed in Flight Mode when possible. Using devices wired instead of using Wi-Fi apparently reduces risks. Use of them in hands-free mode is another useful approach, so that the devices are not so close to youngsters’ heads. We’re not experts ourselves, but these measures seem like sensible precautions.
that the ‘RF wireless radiation’ emitted by Wi-Fi connected screens and devices may carry potential health risks particularly, they argue, for pregnant women, their unborn foetuses and the young. The very young, of course, have brains that are still at a critical development stage. For this reason, the experts concerned advocate that access to devices like mobile phones should be limited, removed from children’s bedrooms at night or, at the very least, placed in Flight Mode when possible. Using devices wired instead of using Wi-Fi apparently reduces risks. Use of them in hands-free mode is another useful approach, so that the devices are not so close to youngsters’ heads. We’re not experts ourselves, but these measures seem like sensible precautions. While time spent by children on connected screens and devices is rising, it’s not all bad news. The pandemic has also seen an increase in the time that parents have been spending with children, including on shared screen viewing as well as on other pastimes like baking, crafts and family activities. At the end of the day, it’s all about a healthy balance and, of course, adult supervision to ensure children’s wellbeing at all times.
While time spent by children on connected screens and devices is rising, it’s not all bad news. The pandemic has also seen an increase in the time that parents have been spending with children, including on shared screen viewing as well as on other pastimes like baking, crafts and family activities. At the end of the day, it’s all about a healthy balance and, of course, adult supervision to ensure children’s wellbeing at all times.

 What are the Recommendations for Early Years Exercise?
What are the Recommendations for Early Years Exercise? What are the Benefits of Early Years Exercise?
What are the Benefits of Early Years Exercise?
 How Parents can Help
How Parents can Help Active Play & Exercise at Little Cedars Day Nursery, Streatham
Active Play & Exercise at Little Cedars Day Nursery, Streatham
 Sensory Play Ideas for Babies
Sensory Play Ideas for Babies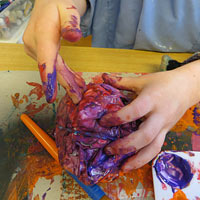 • Paper. Babies will love the feeling of scrunching up paper and will notice the sound as well as the contoured feel of their new creation. They may need a demonstration to get started, though. They’ll start to comprehend the concept that something in one form, like a pristine, wafer-thin sheet of paper, can be made into something completely different — in this case, perhaps a simple ‘ball’ of scrunched-up paper. Even
• Paper. Babies will love the feeling of scrunching up paper and will notice the sound as well as the contoured feel of their new creation. They may need a demonstration to get started, though. They’ll start to comprehend the concept that something in one form, like a pristine, wafer-thin sheet of paper, can be made into something completely different — in this case, perhaps a simple ‘ball’ of scrunched-up paper. Even  • Different objects & materials: babies will enjoy playing and learning about the properties, touch, feel and sound of different objects and materials. For example, (safe) wooden utensils, water in a closed beaker or bottle or small plastic or card boxes that they tap like a drum, or try to stack into a ‘wall’ — and so on. They’ll learn about physical properties of each along the way, including sounds, textures, touch and, if they include some carefully chosen food items, taste. It’s amazing what fun babies will have with such simple items — often learning far more from these than from purchased toys.
• Different objects & materials: babies will enjoy playing and learning about the properties, touch, feel and sound of different objects and materials. For example, (safe) wooden utensils, water in a closed beaker or bottle or small plastic or card boxes that they tap like a drum, or try to stack into a ‘wall’ — and so on. They’ll learn about physical properties of each along the way, including sounds, textures, touch and, if they include some carefully chosen food items, taste. It’s amazing what fun babies will have with such simple items — often learning far more from these than from purchased toys. • The natural world: babies also greatly enjoy the simple pleasures offered by the natural world. A breeze on their faces may greatly intrigue them, even more so when they see leaves rustling and moving a little on the ground. The feel and texture of grass on the lawn or the sight of sunlight dappling through the trees or reflecting off puddles can be wondrous to them. Under close supervision, getting to know the textures, hues and smells of safe, natural objects outdoors can also be a source of sensory discovery.
• The natural world: babies also greatly enjoy the simple pleasures offered by the natural world. A breeze on their faces may greatly intrigue them, even more so when they see leaves rustling and moving a little on the ground. The feel and texture of grass on the lawn or the sight of sunlight dappling through the trees or reflecting off puddles can be wondrous to them. Under close supervision, getting to know the textures, hues and smells of safe, natural objects outdoors can also be a source of sensory discovery.
 • Hand & foot prints: preschoolers will never be bored with smothering their hands or feet in coloured paints, then making prints on paper or card. Footprints and handprints can be random or used to make images or patterns. This process is both creative and a sensory experience for them as the cold paint squelches between fingers or toes. They’ll learn so much including about mixing pigments, creating images from simple printed shapes, about the concept of paint eventually drying to form something semi-permanent and about different textures being formed, depending on the consistency of the paint. We take these discoveries for granted as adults, but we would originally have had to learn about them during our early, formative years.
• Hand & foot prints: preschoolers will never be bored with smothering their hands or feet in coloured paints, then making prints on paper or card. Footprints and handprints can be random or used to make images or patterns. This process is both creative and a sensory experience for them as the cold paint squelches between fingers or toes. They’ll learn so much including about mixing pigments, creating images from simple printed shapes, about the concept of paint eventually drying to form something semi-permanent and about different textures being formed, depending on the consistency of the paint. We take these discoveries for granted as adults, but we would originally have had to learn about them during our early, formative years. • Food creativity: toddlers can also take playing with food to the next level by introducing the concept of making images out of things like fruit- or vegetable-based sauces, cream or yogurt. Whole pictures can be made of food, using the hands, for example using broccoli for ‘trees’, peas for grassy areas and so on. The whole thing can smell great and even be tasted! Playing, hands-on, with food in this way can be fun and creative but also help children learn to accept new foods and tastes into their diets. However, care needs to be taken because proper mealtimes require good manners and children need to understand that food is not usually for playing with.
• Food creativity: toddlers can also take playing with food to the next level by introducing the concept of making images out of things like fruit- or vegetable-based sauces, cream or yogurt. Whole pictures can be made of food, using the hands, for example using broccoli for ‘trees’, peas for grassy areas and so on. The whole thing can smell great and even be tasted! Playing, hands-on, with food in this way can be fun and creative but also help children learn to accept new foods and tastes into their diets. However, care needs to be taken because proper mealtimes require good manners and children need to understand that food is not usually for playing with. • Sensory sand: it’s very rare for little ones to dislike playing with sand, which allows youngsters to get hands-on creatively. They can learn about the unique and varying textures, consistencies and properties of sand, depending on how much moisture it contains. Dry sand has its own unique set of properties, acting and feeling almost like a powder. Very runny, wet sand is great fun as it can be used to run through the hands and ‘set’ into pointy mountain shapes that look quite magical. Or, when less water is added, sand can be fashioned into shapes and, of course, “castles”, using the hands or by filling buckets, hollow vessels, or tubs. Children can also press their hands and feet into level, damp sand in a sandpit or tray, to make impressions and patterns. It feels great too and is an almost essential part of childhood. Young children learn so much from this stimulating, multi-sensory type of play.
• Sensory sand: it’s very rare for little ones to dislike playing with sand, which allows youngsters to get hands-on creatively. They can learn about the unique and varying textures, consistencies and properties of sand, depending on how much moisture it contains. Dry sand has its own unique set of properties, acting and feeling almost like a powder. Very runny, wet sand is great fun as it can be used to run through the hands and ‘set’ into pointy mountain shapes that look quite magical. Or, when less water is added, sand can be fashioned into shapes and, of course, “castles”, using the hands or by filling buckets, hollow vessels, or tubs. Children can also press their hands and feet into level, damp sand in a sandpit or tray, to make impressions and patterns. It feels great too and is an almost essential part of childhood. Young children learn so much from this stimulating, multi-sensory type of play. • Playing with dough: whether bought or home-made, dough is always a big hit with young children. It can be fashioned with the hands into shapes, characters, animals and mini-sculptures. Using food colouring in dough also allows children to discover more about mixing pigments. Salt dough can also be baked (under the close supervision of an adult) so that it hardens into more permanent creations. Many types of dough even smell great too! What’s more, it can even lead to a bigger interest in cooking real, edible dough and other baked foods when they’re a little older.
• Playing with dough: whether bought or home-made, dough is always a big hit with young children. It can be fashioned with the hands into shapes, characters, animals and mini-sculptures. Using food colouring in dough also allows children to discover more about mixing pigments. Salt dough can also be baked (under the close supervision of an adult) so that it hardens into more permanent creations. Many types of dough even smell great too! What’s more, it can even lead to a bigger interest in cooking real, edible dough and other baked foods when they’re a little older. • A sensory garden. We’ve left perhaps the best until last. Making a sensory garden area with, or for, little ones will give them a magical experience. There are so many materials that can be used in the construction of sensory gardens, including soil, earth, pea shingle, tree bark, moss and so on. Plants themselves will also add to the fascinating mixture of textures, colours and even smells found within a sensory garden. It can be as small or large as you have room for and can even be achieved in containers, pots or on balconies for those who do not have gardens. It can take many forms so it’s design also gives children a wonderful creative opportunity. Sensory gardens are a complete feast for the senses for young children — adults too — encompassing touch (e.g. the textures of materials, moss and plants), smell (why not include some herbs — these smell wonderful and can be tasted too), potentially sound (crunchy gravel, rustling leaves etc.), sight (aesthetics, colour etc.) and will also give children ample opportunity to improve balance and body awareness as they construct and create in this unique space.
• A sensory garden. We’ve left perhaps the best until last. Making a sensory garden area with, or for, little ones will give them a magical experience. There are so many materials that can be used in the construction of sensory gardens, including soil, earth, pea shingle, tree bark, moss and so on. Plants themselves will also add to the fascinating mixture of textures, colours and even smells found within a sensory garden. It can be as small or large as you have room for and can even be achieved in containers, pots or on balconies for those who do not have gardens. It can take many forms so it’s design also gives children a wonderful creative opportunity. Sensory gardens are a complete feast for the senses for young children — adults too — encompassing touch (e.g. the textures of materials, moss and plants), smell (why not include some herbs — these smell wonderful and can be tasted too), potentially sound (crunchy gravel, rustling leaves etc.), sight (aesthetics, colour etc.) and will also give children ample opportunity to improve balance and body awareness as they construct and create in this unique space.