
 Despite many dyslexic people being highly intelligent, dyslexia makes it difficult for them to recognise words and/or be able to break them down into their smaller components. It is recognised as a Specific Learning Difficulty (‘SpLD’) and can seriously affect their education if not recognised and addressed early.
Despite many dyslexic people being highly intelligent, dyslexia makes it difficult for them to recognise words and/or be able to break them down into their smaller components. It is recognised as a Specific Learning Difficulty (‘SpLD’) and can seriously affect their education if not recognised and addressed early.
A dictionary defines dyslexia as “a general term for disorders that involve difficulty in learning to read or interpret words, letters, and other symbols, but that do not affect general intelligence”. When it first came to the attention of doctors in the late 19th Century, it was more commonly referred to as “Word Blindness”, which pretty much sums up how dyslexia affects people afflicted by it.
The Adverse Effects of Dyslexia
 Such an affliction can have profound implications for a person. It will adversely affect their reading, writing and comprehension, thereby limiting their overall learning capability and hindering overall literacy. These are particularly critical skills during their early years as that’s at the start of their education, when the knock-on effects of such limiting factors will be at their most significant. It will slow down their progress in many topics and areas of education, also leading potentially to lower self-confidence and possibly even getting them mislabelled as ‘slow’ or ‘lazy’ by the unenlightened. Ultimately, it can severely limit their potential careers and life outcomes.
Such an affliction can have profound implications for a person. It will adversely affect their reading, writing and comprehension, thereby limiting their overall learning capability and hindering overall literacy. These are particularly critical skills during their early years as that’s at the start of their education, when the knock-on effects of such limiting factors will be at their most significant. It will slow down their progress in many topics and areas of education, also leading potentially to lower self-confidence and possibly even getting them mislabelled as ‘slow’ or ‘lazy’ by the unenlightened. Ultimately, it can severely limit their potential careers and life outcomes.
Those are incredibly unfair ramifications and that’s why we are taking a closer look at how parents, carers and education professionals can learn to spot the signs of dyslexia early, so that dyslexic children can be helped as soon as possible.
“The earlier a child with dyslexia is diagnosed, the more effective educational interventions are likely to be.” (NHS)
Early Warning Signs of Possible Dyslexia
In pre-school children, there are several things to watch out for. These include:
 Children finding it difficult to learn the alphabet;
Children finding it difficult to learn the alphabet;- Little interest in attempting to do so;
- Difficulty pronouncing multi-syllable words (or phrases) including jumbling the the order of them — ‘flutterby’ instead of ‘butterfly’ for example;
- Difficulty with rhyming words and even nursery rhymes;
- Slower speech development compared to others in their year group;
- Finding it difficult to express themselves verbally, including jumbling word order in sentences and having trouble recalling appropriate word(s) to use;
- Slower development of fine motor skills, for example maintaining a regular rhythm on a percussive instrument.
We should add, though, that having any or even all of these problems does not, in itself, definitely mean that the child has dyslexia — they are just possible signs of it. Many children without dyslexia may have some of these symptoms, so it’s important not to jump to incorrect conclusions. The symptoms of dyslexia also vary greatly from person to person, so diagnosis is not easy.
Dyslexia Signs in School-Age Children
It may become easier to diagnose dyslexia in children once they start school, as they will be reading and writing more by that time. Signs of possible dyslexia to add to the list above may then include:
 The child describing words and letters as visually jumbling, blurring or even moving around when they try to read them;
The child describing words and letters as visually jumbling, blurring or even moving around when they try to read them;- Giving poor written answers but good verbal ones;
- Difficulty learning common sequences of words like months of the year, days in the week and, as we mentioned before, letters of the alphabet;
- Difficulty following a sequence of instructions given at the same time (e.g. ‘put the fork on the plate, then take it to the kitchen’), but being OK if they are given separately;
- Inconsistent spelling and incorrect letter order;
- Mistaking numbers and letters for one another, for example using p instead of d or 9 instead of 6;
- Slow reading and writing speeds, poor quality of handwriting and making mistakes when reading out loud;
- A lower-than-average grasp of phonetics, phonology and ‘word attack’ skills, that might otherwise have helped a child to work out the possible meaning of multi-syllable/multi-part words through attention to the individual parts.
Learn more about assessment and diagnosis of dyslexia on the NHS site.
Is There a Cure for Dyslexia?
 There is no cure for dyslexia, but measures to mitigate its effects can be taken by education professionals, parents, carers and even those affected by it. It’s incredibly important, though, for both parents and education professionals to try to recognise it early, for example at nursery or pre-school, so that a suitable teaching programme can be introduced as early as possible.
There is no cure for dyslexia, but measures to mitigate its effects can be taken by education professionals, parents, carers and even those affected by it. It’s incredibly important, though, for both parents and education professionals to try to recognise it early, for example at nursery or pre-school, so that a suitable teaching programme can be introduced as early as possible.
Dyslexia & Special Needs at Little Cedars Nursery
If staff or parents of children at our nursery suspect that a child may be dyslexic — or have any other special needs — it’s important to discuss it together as early as possible in the child’s education. In this way, an appropriate learning and development programme can be agreed; one that is tailored to suit the individual child’s needs, in the best possible way. Doing so as early as possible, ideally starting in their pre-school years, will help to limit any adverse effects caused by the condition. When properly addressed, there is no reason why a child with dyslexia shouldn’t be able to absolutely thrive, despite the condition. It goes without saying that we are always happy to discuss any concerns parents may have about their children — indeed we encourage it so that we can work together to address such concerns.
 Little Cedars is an outstanding nursery in Streatham SW16, near Streatham Common, Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Furzedown, Tooting and Balham. If you are looking for high quality nurseries or pre-schools in any of these areas, please get in touch and we’d be delighted to show you and your child/children around, so you can see the wonderful nursery facilities, happy children and exceptionally professional staff for yourself. Please get in touch, while a few places are still available, via one of the following:
Little Cedars is an outstanding nursery in Streatham SW16, near Streatham Common, Streatham Hill, Streatham Park, Furzedown, Tooting and Balham. If you are looking for high quality nurseries or pre-schools in any of these areas, please get in touch and we’d be delighted to show you and your child/children around, so you can see the wonderful nursery facilities, happy children and exceptionally professional staff for yourself. Please get in touch, while a few places are still available, via one of the following:

 Children finding it difficult to learn the alphabet;
Children finding it difficult to learn the alphabet; The child describing words and letters as visually jumbling, blurring or even moving around when they try to read them;
The child describing words and letters as visually jumbling, blurring or even moving around when they try to read them;
 The EYFS framework sets the statutory approach required for pretty much every aspect of early years childcare and education provision in the UK. The standards cover the learning and development programmes, learning goals, approach to assessment, safeguarding, welfare of children, staffing, and much more. In this guide, however, we’ll focus purely on the 7 key areas of learning and development covered by the EYFS. Essentially, these form the core curriculum at nurseries like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Let’s take a look …
The EYFS framework sets the statutory approach required for pretty much every aspect of early years childcare and education provision in the UK. The standards cover the learning and development programmes, learning goals, approach to assessment, safeguarding, welfare of children, staffing, and much more. In this guide, however, we’ll focus purely on the 7 key areas of learning and development covered by the EYFS. Essentially, these form the core curriculum at nurseries like Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Let’s take a look … It would be hard to overstate the importance of good communication and language skills, as they underpin early years progress in just about everything else. So, early years providers like Little Cedars encourage two-way interactions and language-rich communications between staff and children right from the outset. Childcare professionals will introduce new vocabulary regularly and help children to understand it and use it themselves through activities like story-telling, role play and question-and-answer sessions. Practitioners will regularly read with (not just to) children, using a wide variety of high quality reading materials, encouraging feedback and engagement from the children as they progress. In this way, new vocabulary is embedded, conversations come naturally and children will thrive in their language and communication skills.
It would be hard to overstate the importance of good communication and language skills, as they underpin early years progress in just about everything else. So, early years providers like Little Cedars encourage two-way interactions and language-rich communications between staff and children right from the outset. Childcare professionals will introduce new vocabulary regularly and help children to understand it and use it themselves through activities like story-telling, role play and question-and-answer sessions. Practitioners will regularly read with (not just to) children, using a wide variety of high quality reading materials, encouraging feedback and engagement from the children as they progress. In this way, new vocabulary is embedded, conversations come naturally and children will thrive in their language and communication skills. Physical development is, of course, another key skill that is foundational for children. After all, it impacts on health, mobility, strength, fitness, agility, coordination, wellbeing and general happiness. So, great care is taken at nurseries like Little Cedars to help children hone their physical skills and development incrementally, to improve all of the above. This is done through the EYFS programmes that are set and customised for each individual child. Skills like balance, gross and fine motor skills, coordination, spatial awareness, hand/eye coordination, strength and agility will therefore gradually improve and become second nature to each child as they grow. Active children will generally become more healthy children. They will also improve social skills and confidence through the activities that they participate in alongside peers. It is also, of course, great fun!
Physical development is, of course, another key skill that is foundational for children. After all, it impacts on health, mobility, strength, fitness, agility, coordination, wellbeing and general happiness. So, great care is taken at nurseries like Little Cedars to help children hone their physical skills and development incrementally, to improve all of the above. This is done through the EYFS programmes that are set and customised for each individual child. Skills like balance, gross and fine motor skills, coordination, spatial awareness, hand/eye coordination, strength and agility will therefore gradually improve and become second nature to each child as they grow. Active children will generally become more healthy children. They will also improve social skills and confidence through the activities that they participate in alongside peers. It is also, of course, great fun! Health, happiness and even the development of early years cognitive function are all underpinned by children’s personal, social and emotional development (‘PSED’). Indeed, PSED forms the backbone of children’s relationships to all adults and peers around them — and also governs how they feel they fit in. That’s all incredibly important, so childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery approach PSED as a ‘prime’ element within the EYFS curriculum. The result is that children are supported and support one another, they learn how to manage emotions and behaviours, how to eat healthy diets, look after themselves physically, and independently manage their own personal needs. All of this will have the knock-on effect of improving confidence and self-esteem and even allow them to set some of their own goals. Close bonds will be made with both staff and other children and conflicts will be more easily resolved peaceably.
Health, happiness and even the development of early years cognitive function are all underpinned by children’s personal, social and emotional development (‘PSED’). Indeed, PSED forms the backbone of children’s relationships to all adults and peers around them — and also governs how they feel they fit in. That’s all incredibly important, so childcare settings like Little Cedars Nursery approach PSED as a ‘prime’ element within the EYFS curriculum. The result is that children are supported and support one another, they learn how to manage emotions and behaviours, how to eat healthy diets, look after themselves physically, and independently manage their own personal needs. All of this will have the knock-on effect of improving confidence and self-esteem and even allow them to set some of their own goals. Close bonds will be made with both staff and other children and conflicts will be more easily resolved peaceably. Reading and writing are crucial elements within every child’s education. Without these skills, learning about other topics would become much more difficult. Literacy is therefore a key area of focus within the EYFS learning and development framework. Like other nurseries, pre-schools and childcare settings that adhere to the EYFS approach, Little Cedars Nursery will therefore endeavour to encourage a love of reading within every child. Reading teaches children to comprehend language, vocabulary, grammar and spelling as well as learning more about the underlying topics themselves.
Reading and writing are crucial elements within every child’s education. Without these skills, learning about other topics would become much more difficult. Literacy is therefore a key area of focus within the EYFS learning and development framework. Like other nurseries, pre-schools and childcare settings that adhere to the EYFS approach, Little Cedars Nursery will therefore endeavour to encourage a love of reading within every child. Reading teaches children to comprehend language, vocabulary, grammar and spelling as well as learning more about the underlying topics themselves. Nurseries, pre-schools, kindergartens and other childcare settings also recognise the importance of mathematics within children’s learning and development. The EYFS curriculum caters well for this, encouraging early years professionals to help children master counting first to 10 and later to 20 and beyond. Children will learn the patterns around numbers, including recognition of odd and even numbers, along with skills like simple addition and subtraction, and the ability to recognise low quantities without having to count. They will also learn to recognise when one quantity is more than, less than or equal to another. In so doing, children will also learn the vocabulary around mathematics in readiness for school once they leave their early years setting.
Nurseries, pre-schools, kindergartens and other childcare settings also recognise the importance of mathematics within children’s learning and development. The EYFS curriculum caters well for this, encouraging early years professionals to help children master counting first to 10 and later to 20 and beyond. Children will learn the patterns around numbers, including recognition of odd and even numbers, along with skills like simple addition and subtraction, and the ability to recognise low quantities without having to count. They will also learn to recognise when one quantity is more than, less than or equal to another. In so doing, children will also learn the vocabulary around mathematics in readiness for school once they leave their early years setting. A good early years education is nothing unless children understand the world around them. The EYFS framework used by early years nurseries like Little Cedars builds in programmes to help children learn more about the world. This includes helping them to learn how to observe, recognise, describe and even draw what’s immediately around them as well as exposing them to environments like the natural world, local parks and museums. It even teaches them to recognise similarities and differences between other cultures, religions and communities in the UK and lives being lived abroad. They will get to know more about people’s roles in society too, for example through visits from police officers, firefighters and nurses. A broad range of written material (both fiction and non-fiction) will inform them further. Topics explored will touch on culture, technology, ecology, religion, community, nature and much, much more. This will enrich their knowledge and understanding of the world they live within, giving context to what they see, hear and read about as they grow older.
A good early years education is nothing unless children understand the world around them. The EYFS framework used by early years nurseries like Little Cedars builds in programmes to help children learn more about the world. This includes helping them to learn how to observe, recognise, describe and even draw what’s immediately around them as well as exposing them to environments like the natural world, local parks and museums. It even teaches them to recognise similarities and differences between other cultures, religions and communities in the UK and lives being lived abroad. They will get to know more about people’s roles in society too, for example through visits from police officers, firefighters and nurses. A broad range of written material (both fiction and non-fiction) will inform them further. Topics explored will touch on culture, technology, ecology, religion, community, nature and much, much more. This will enrich their knowledge and understanding of the world they live within, giving context to what they see, hear and read about as they grow older. Expressive arts and design are also integral elements within the EYFS curriculum. Early years childcare settings like Little Cedars ensure that children are given a wide range of opportunities to be creative and to free their imaginations. A huge variety of media, materials, tools and activities can be used by children to express themselves and communicate both visually and audibly. Colour, texture, form and function are explored along with opportunities for role play, story-telling, poetry, singing, performance and even dancing when appropriate.
Expressive arts and design are also integral elements within the EYFS curriculum. Early years childcare settings like Little Cedars ensure that children are given a wide range of opportunities to be creative and to free their imaginations. A huge variety of media, materials, tools and activities can be used by children to express themselves and communicate both visually and audibly. Colour, texture, form and function are explored along with opportunities for role play, story-telling, poetry, singing, performance and even dancing when appropriate. Little Cedars Nursery (Streatham) uses the EYFS framework to shape the educational activities and programmes that babies and children experience at the nursery. Part of this includes the setting of learning goals that each child needs to work towards as they gradually approach the age of 5, when they will move on to school. These are individual goals, tailored to the unique needs, interests, abilities – and any disabilities – of each individual child. A continuous regime of assessment will be undertaken by staff to monitor each child’s progress during their time with the nursery, with the learning programme adjusted, as necessary, along the way. A ‘Key Person’, allocated to each child, facilitates that assessment proactively. Additionally, staff will regularly engage with parents or carers/guardians to ensure that progress towards the learning and development goals is continued at home, wherever possible. Progress is communicated and a learning journal retained and available to parents at any time. In this way, each child achieves personal bests in all areas and everyone is kept up-to-date with the child’s progress.
Little Cedars Nursery (Streatham) uses the EYFS framework to shape the educational activities and programmes that babies and children experience at the nursery. Part of this includes the setting of learning goals that each child needs to work towards as they gradually approach the age of 5, when they will move on to school. These are individual goals, tailored to the unique needs, interests, abilities – and any disabilities – of each individual child. A continuous regime of assessment will be undertaken by staff to monitor each child’s progress during their time with the nursery, with the learning programme adjusted, as necessary, along the way. A ‘Key Person’, allocated to each child, facilitates that assessment proactively. Additionally, staff will regularly engage with parents or carers/guardians to ensure that progress towards the learning and development goals is continued at home, wherever possible. Progress is communicated and a learning journal retained and available to parents at any time. In this way, each child achieves personal bests in all areas and everyone is kept up-to-date with the child’s progress.

 In April last year, we published a compelling article about
In April last year, we published a compelling article about  Reading with children also makes the task less daunting, particularly for the youngest children. Reading together also makes it more interesting and more fun. When it’s more interesting and more fun, the child is going to enjoy it more and naturally want to read more often — eventually independently — and all of that is priceless as part of their education and general knowledge going forwards. Reading can also bring parent and child closer through the time spent together. It can be great fun for the adult too, particularly when the child gets older and adults are exposed to classic children’s books that perhaps they were not, themselves, exposed to when they were young.
Reading with children also makes the task less daunting, particularly for the youngest children. Reading together also makes it more interesting and more fun. When it’s more interesting and more fun, the child is going to enjoy it more and naturally want to read more often — eventually independently — and all of that is priceless as part of their education and general knowledge going forwards. Reading can also bring parent and child closer through the time spent together. It can be great fun for the adult too, particularly when the child gets older and adults are exposed to classic children’s books that perhaps they were not, themselves, exposed to when they were young. The Nuffield Foundation’s mission is to advance social wellbeing and educational opportunity. In a partnership with the University of Newcastle, the foundation funded a deep study
The Nuffield Foundation’s mission is to advance social wellbeing and educational opportunity. In a partnership with the University of Newcastle, the foundation funded a deep study It will come as no surprise, therefore, to learn that we put all of the above into practice at Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Getting closely involved in children’s reading, using a huge variety of reading material in an interactive way, gives our nursery children the very best start in life. Indeed, our childcare professionals prepare them thoroughly for school by the time they leave us. They take with them reading, writing, literacy, language, vocabulary and self-expression skills in the process — and all this accomplished at least in part through guided reading.
It will come as no surprise, therefore, to learn that we put all of the above into practice at Little Cedars Nursery in Streatham. Getting closely involved in children’s reading, using a huge variety of reading material in an interactive way, gives our nursery children the very best start in life. Indeed, our childcare professionals prepare them thoroughly for school by the time they leave us. They take with them reading, writing, literacy, language, vocabulary and self-expression skills in the process — and all this accomplished at least in part through guided reading.
 What are the Recommendations for Early Years Exercise?
What are the Recommendations for Early Years Exercise? What are the Benefits of Early Years Exercise?
What are the Benefits of Early Years Exercise?
 How Parents can Help
How Parents can Help Active Play & Exercise at Little Cedars Day Nursery, Streatham
Active Play & Exercise at Little Cedars Day Nursery, Streatham
 Sensory Play Ideas for Babies
Sensory Play Ideas for Babies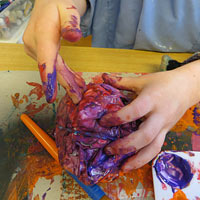 • Paper. Babies will love the feeling of scrunching up paper and will notice the sound as well as the contoured feel of their new creation. They may need a demonstration to get started, though. They’ll start to comprehend the concept that something in one form, like a pristine, wafer-thin sheet of paper, can be made into something completely different — in this case, perhaps a simple ‘ball’ of scrunched-up paper. Even
• Paper. Babies will love the feeling of scrunching up paper and will notice the sound as well as the contoured feel of their new creation. They may need a demonstration to get started, though. They’ll start to comprehend the concept that something in one form, like a pristine, wafer-thin sheet of paper, can be made into something completely different — in this case, perhaps a simple ‘ball’ of scrunched-up paper. Even  • Different objects & materials: babies will enjoy playing and learning about the properties, touch, feel and sound of different objects and materials. For example, (safe) wooden utensils, water in a closed beaker or bottle or small plastic or card boxes that they tap like a drum, or try to stack into a ‘wall’ — and so on. They’ll learn about physical properties of each along the way, including sounds, textures, touch and, if they include some carefully chosen food items, taste. It’s amazing what fun babies will have with such simple items — often learning far more from these than from purchased toys.
• Different objects & materials: babies will enjoy playing and learning about the properties, touch, feel and sound of different objects and materials. For example, (safe) wooden utensils, water in a closed beaker or bottle or small plastic or card boxes that they tap like a drum, or try to stack into a ‘wall’ — and so on. They’ll learn about physical properties of each along the way, including sounds, textures, touch and, if they include some carefully chosen food items, taste. It’s amazing what fun babies will have with such simple items — often learning far more from these than from purchased toys. • The natural world: babies also greatly enjoy the simple pleasures offered by the natural world. A breeze on their faces may greatly intrigue them, even more so when they see leaves rustling and moving a little on the ground. The feel and texture of grass on the lawn or the sight of sunlight dappling through the trees or reflecting off puddles can be wondrous to them. Under close supervision, getting to know the textures, hues and smells of safe, natural objects outdoors can also be a source of sensory discovery.
• The natural world: babies also greatly enjoy the simple pleasures offered by the natural world. A breeze on their faces may greatly intrigue them, even more so when they see leaves rustling and moving a little on the ground. The feel and texture of grass on the lawn or the sight of sunlight dappling through the trees or reflecting off puddles can be wondrous to them. Under close supervision, getting to know the textures, hues and smells of safe, natural objects outdoors can also be a source of sensory discovery.
 • Hand & foot prints: preschoolers will never be bored with smothering their hands or feet in coloured paints, then making prints on paper or card. Footprints and handprints can be random or used to make images or patterns. This process is both creative and a sensory experience for them as the cold paint squelches between fingers or toes. They’ll learn so much including about mixing pigments, creating images from simple printed shapes, about the concept of paint eventually drying to form something semi-permanent and about different textures being formed, depending on the consistency of the paint. We take these discoveries for granted as adults, but we would originally have had to learn about them during our early, formative years.
• Hand & foot prints: preschoolers will never be bored with smothering their hands or feet in coloured paints, then making prints on paper or card. Footprints and handprints can be random or used to make images or patterns. This process is both creative and a sensory experience for them as the cold paint squelches between fingers or toes. They’ll learn so much including about mixing pigments, creating images from simple printed shapes, about the concept of paint eventually drying to form something semi-permanent and about different textures being formed, depending on the consistency of the paint. We take these discoveries for granted as adults, but we would originally have had to learn about them during our early, formative years. • Food creativity: toddlers can also take playing with food to the next level by introducing the concept of making images out of things like fruit- or vegetable-based sauces, cream or yogurt. Whole pictures can be made of food, using the hands, for example using broccoli for ‘trees’, peas for grassy areas and so on. The whole thing can smell great and even be tasted! Playing, hands-on, with food in this way can be fun and creative but also help children learn to accept new foods and tastes into their diets. However, care needs to be taken because proper mealtimes require good manners and children need to understand that food is not usually for playing with.
• Food creativity: toddlers can also take playing with food to the next level by introducing the concept of making images out of things like fruit- or vegetable-based sauces, cream or yogurt. Whole pictures can be made of food, using the hands, for example using broccoli for ‘trees’, peas for grassy areas and so on. The whole thing can smell great and even be tasted! Playing, hands-on, with food in this way can be fun and creative but also help children learn to accept new foods and tastes into their diets. However, care needs to be taken because proper mealtimes require good manners and children need to understand that food is not usually for playing with. • Sensory sand: it’s very rare for little ones to dislike playing with sand, which allows youngsters to get hands-on creatively. They can learn about the unique and varying textures, consistencies and properties of sand, depending on how much moisture it contains. Dry sand has its own unique set of properties, acting and feeling almost like a powder. Very runny, wet sand is great fun as it can be used to run through the hands and ‘set’ into pointy mountain shapes that look quite magical. Or, when less water is added, sand can be fashioned into shapes and, of course, “castles”, using the hands or by filling buckets, hollow vessels, or tubs. Children can also press their hands and feet into level, damp sand in a sandpit or tray, to make impressions and patterns. It feels great too and is an almost essential part of childhood. Young children learn so much from this stimulating, multi-sensory type of play.
• Sensory sand: it’s very rare for little ones to dislike playing with sand, which allows youngsters to get hands-on creatively. They can learn about the unique and varying textures, consistencies and properties of sand, depending on how much moisture it contains. Dry sand has its own unique set of properties, acting and feeling almost like a powder. Very runny, wet sand is great fun as it can be used to run through the hands and ‘set’ into pointy mountain shapes that look quite magical. Or, when less water is added, sand can be fashioned into shapes and, of course, “castles”, using the hands or by filling buckets, hollow vessels, or tubs. Children can also press their hands and feet into level, damp sand in a sandpit or tray, to make impressions and patterns. It feels great too and is an almost essential part of childhood. Young children learn so much from this stimulating, multi-sensory type of play. • Playing with dough: whether bought or home-made, dough is always a big hit with young children. It can be fashioned with the hands into shapes, characters, animals and mini-sculptures. Using food colouring in dough also allows children to discover more about mixing pigments. Salt dough can also be baked (under the close supervision of an adult) so that it hardens into more permanent creations. Many types of dough even smell great too! What’s more, it can even lead to a bigger interest in cooking real, edible dough and other baked foods when they’re a little older.
• Playing with dough: whether bought or home-made, dough is always a big hit with young children. It can be fashioned with the hands into shapes, characters, animals and mini-sculptures. Using food colouring in dough also allows children to discover more about mixing pigments. Salt dough can also be baked (under the close supervision of an adult) so that it hardens into more permanent creations. Many types of dough even smell great too! What’s more, it can even lead to a bigger interest in cooking real, edible dough and other baked foods when they’re a little older. • A sensory garden. We’ve left perhaps the best until last. Making a sensory garden area with, or for, little ones will give them a magical experience. There are so many materials that can be used in the construction of sensory gardens, including soil, earth, pea shingle, tree bark, moss and so on. Plants themselves will also add to the fascinating mixture of textures, colours and even smells found within a sensory garden. It can be as small or large as you have room for and can even be achieved in containers, pots or on balconies for those who do not have gardens. It can take many forms so it’s design also gives children a wonderful creative opportunity. Sensory gardens are a complete feast for the senses for young children — adults too — encompassing touch (e.g. the textures of materials, moss and plants), smell (why not include some herbs — these smell wonderful and can be tasted too), potentially sound (crunchy gravel, rustling leaves etc.), sight (aesthetics, colour etc.) and will also give children ample opportunity to improve balance and body awareness as they construct and create in this unique space.
• A sensory garden. We’ve left perhaps the best until last. Making a sensory garden area with, or for, little ones will give them a magical experience. There are so many materials that can be used in the construction of sensory gardens, including soil, earth, pea shingle, tree bark, moss and so on. Plants themselves will also add to the fascinating mixture of textures, colours and even smells found within a sensory garden. It can be as small or large as you have room for and can even be achieved in containers, pots or on balconies for those who do not have gardens. It can take many forms so it’s design also gives children a wonderful creative opportunity. Sensory gardens are a complete feast for the senses for young children — adults too — encompassing touch (e.g. the textures of materials, moss and plants), smell (why not include some herbs — these smell wonderful and can be tasted too), potentially sound (crunchy gravel, rustling leaves etc.), sight (aesthetics, colour etc.) and will also give children ample opportunity to improve balance and body awareness as they construct and create in this unique space.
 Sensory play is incredibly important for under-fives. Babies and young children benefit enormously when their play activities stimulate the senses and in this article we’ll explore those benefits in some detail.
Sensory play is incredibly important for under-fives. Babies and young children benefit enormously when their play activities stimulate the senses and in this article we’ll explore those benefits in some detail. activities that involve touch, where babies and children can acquaint themselves with the feelings of temperature, softness, hardness, pressure, vibration, roughness, smoothness etc.;
activities that involve touch, where babies and children can acquaint themselves with the feelings of temperature, softness, hardness, pressure, vibration, roughness, smoothness etc.; The Benefits of Sensory Play
The Benefits of Sensory Play Babies and children are, of course, given a huge variety of sensory-based play opportunities at
Babies and children are, of course, given a huge variety of sensory-based play opportunities at 
 A Convenient Nursery Location
A Convenient Nursery Location Compatible Opening Hours
Compatible Opening Hours Visit the Nurseries & Ask Questions
Visit the Nurseries & Ask Questions Nursery Security & Safeguarding
Nursery Security & Safeguarding
 Let’s first go back to the beginning. A sense of humour is apparently a learned aspect of a person’s character, to a fair extent. It’s something that develops and changes as a child gets older, rather than something they’re born with as a result of their DNA. As such, it’s important that babies and young children are given every opportunity to enjoy laughter and, while doing so, have fun with those around them. Laughing also is also closely linked to happiness, and being happy is, of course, priceless.
Let’s first go back to the beginning. A sense of humour is apparently a learned aspect of a person’s character, to a fair extent. It’s something that develops and changes as a child gets older, rather than something they’re born with as a result of their DNA. As such, it’s important that babies and young children are given every opportunity to enjoy laughter and, while doing so, have fun with those around them. Laughing also is also closely linked to happiness, and being happy is, of course, priceless. Laughing helps children to develop better self-esteem;
Laughing helps children to develop better self-esteem; Improves mental health;
Improves mental health; The staff at
The staff at 

 These are significant benefits, so high quality sleep — and the right amount — is incredibly important.
These are significant benefits, so high quality sleep — and the right amount — is incredibly important. ‘Sleep Hygiene‘ is a term that refers to the whole routine around bedtime and sleeping, including important preparation measures during the run-up to bedtime A good sleep hygiene regime will help children get to sleep and to sleep soundly.
‘Sleep Hygiene‘ is a term that refers to the whole routine around bedtime and sleeping, including important preparation measures during the run-up to bedtime A good sleep hygiene regime will help children get to sleep and to sleep soundly. The biggest message is that setting up — and sticking to — a set bedtime routine will greatly help with the quality of your child’s sleep. It sets a pattern that their minds and bodies will become used to naturally. A regime of this nature can include winding-down activities like a warm bath or shower, a peaceful book-reading session, dimmed lights and so on in the approach to bedtime. The routine will prepare them automatically for sleep even during the run-up to actually sleeping.
The biggest message is that setting up — and sticking to — a set bedtime routine will greatly help with the quality of your child’s sleep. It sets a pattern that their minds and bodies will become used to naturally. A regime of this nature can include winding-down activities like a warm bath or shower, a peaceful book-reading session, dimmed lights and so on in the approach to bedtime. The routine will prepare them automatically for sleep even during the run-up to actually sleeping. At Little Cedars Day Nursery in Streatham, we understand the importance of sleep, particularly for babies and the youngest of the children. For that reason, we ensure that children have the opportunity of a nap both in the morning and in the afternoon. For example, babies sleep for about half an hour to an hour around 9.30am and then again after lunch, for 1 to 2 hours between about 1pm and 3pm. Preschoolers don’t have to sleep if they don’t want to, but are given the opportunity to do so — every child is different. We also take a lead from parents who may prefer their child to keep to a particular sleep pattern. If you would like more information about this topic, and how we approach it at the nursery, please do get in touch.
At Little Cedars Day Nursery in Streatham, we understand the importance of sleep, particularly for babies and the youngest of the children. For that reason, we ensure that children have the opportunity of a nap both in the morning and in the afternoon. For example, babies sleep for about half an hour to an hour around 9.30am and then again after lunch, for 1 to 2 hours between about 1pm and 3pm. Preschoolers don’t have to sleep if they don’t want to, but are given the opportunity to do so — every child is different. We also take a lead from parents who may prefer their child to keep to a particular sleep pattern. If you would like more information about this topic, and how we approach it at the nursery, please do get in touch.